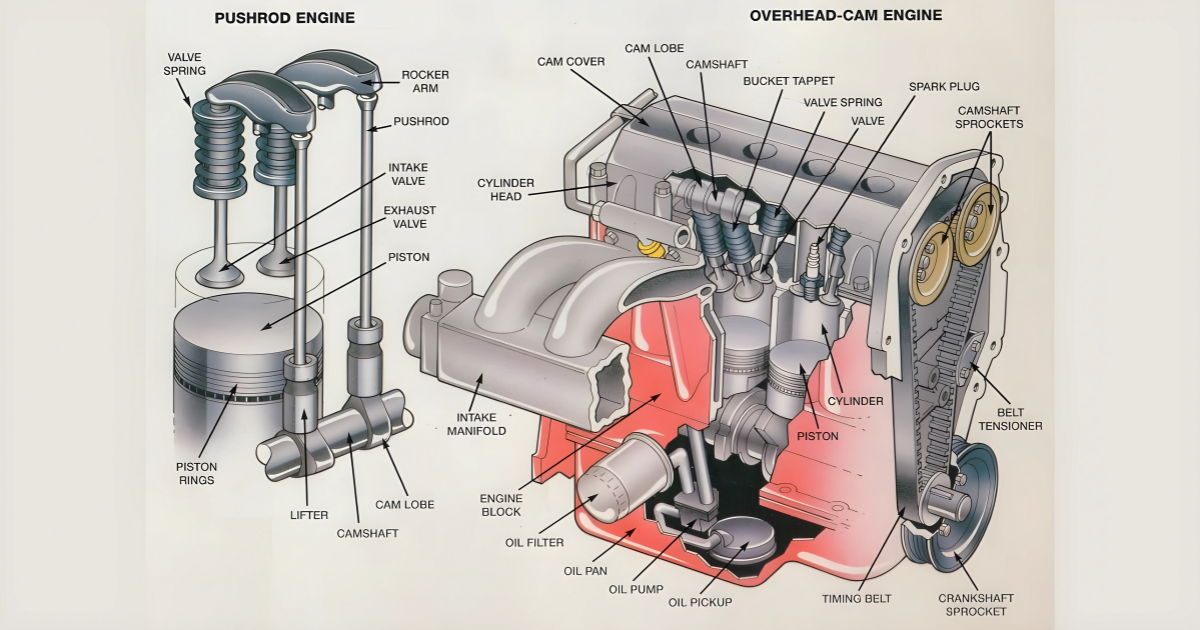
Pistons are essential components in internal combustion engines. They have the crucial function of converting fuel into motion, which powers vehicles and machinery. Despite their unassuming cylindrical shape, these devices are made up of intricate components that function together to endure high temperatures and pressure.
Now, let’s explore the fascinating world of piston parts, uncovering the incredible engineering behind the power that drives our cars and many other machines.
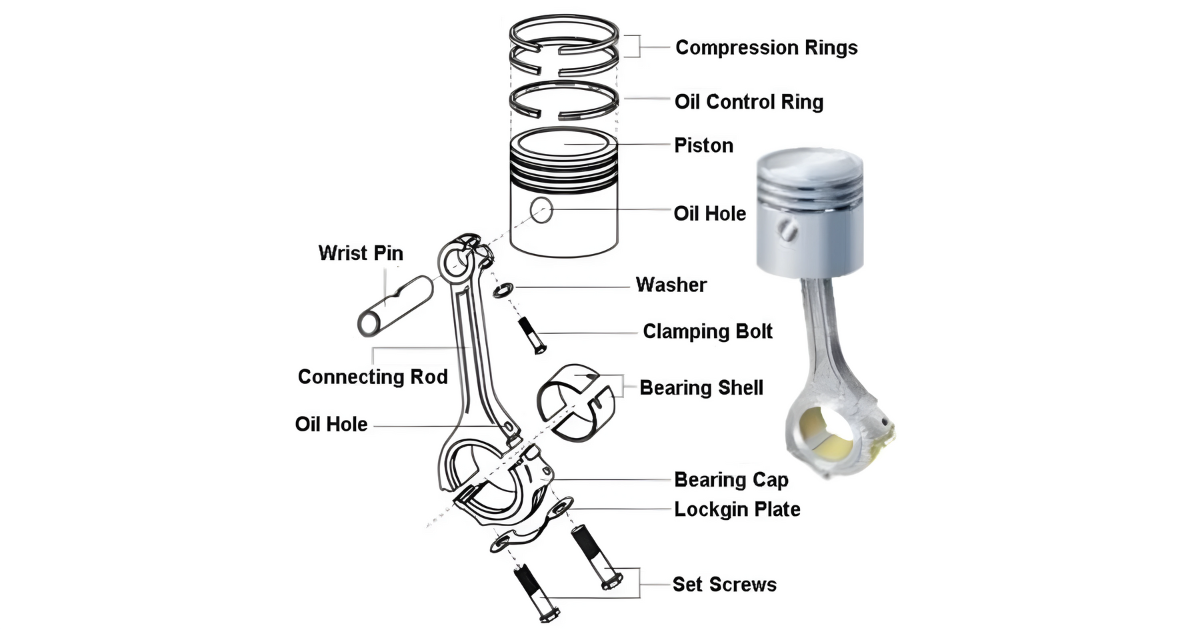
Piston Body
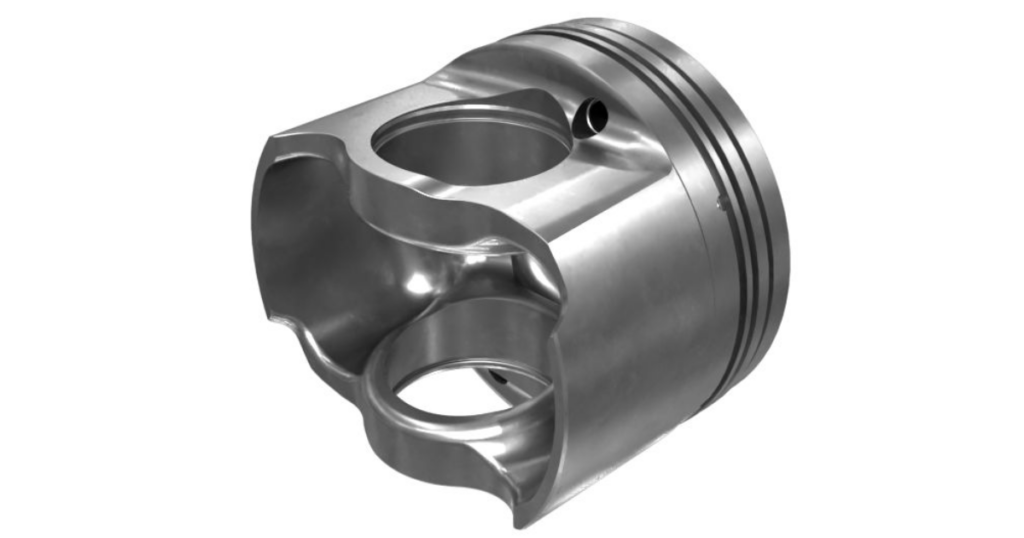

The piston is made from a lightweight aluminum alloy and serves as the main component. This part rotates within the engine cylinder, enabling the engine to operate smoothly. Aluminum alloys are popular due to their lightweight nature, excellent heat conductivity, and impressive durability. High-performance engines often use forged or coated pistons to increase strength and reduce friction.
Crown
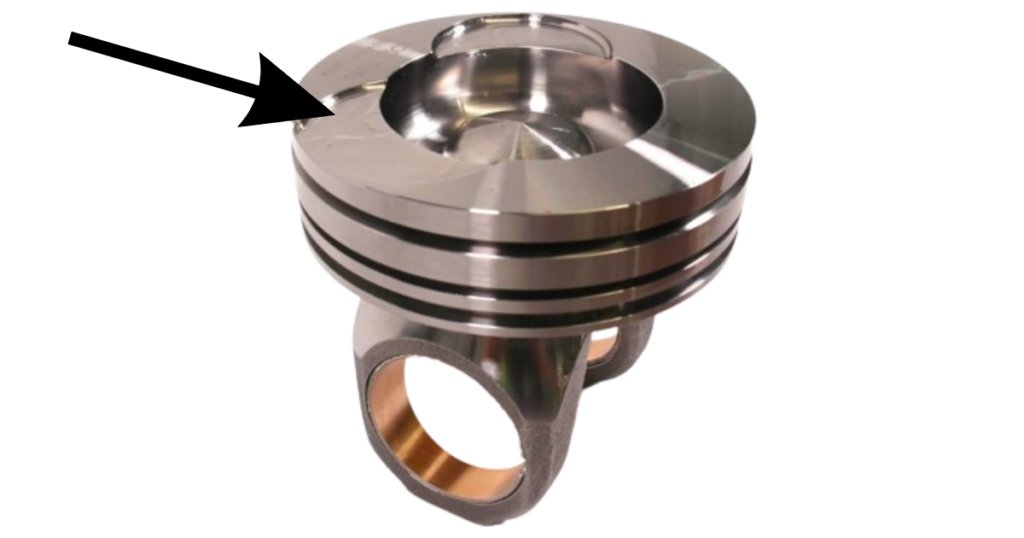

The top surface of the piston, known as the crown, is a crucial part that experiences high temperatures and pressures during combustion. This section needs to withstand the pressure from expanding gases. In order to improve performance, the crown of the engine often includes complex designs that help with fuel combustion and efficient energy transfer within the engine.
Skirt
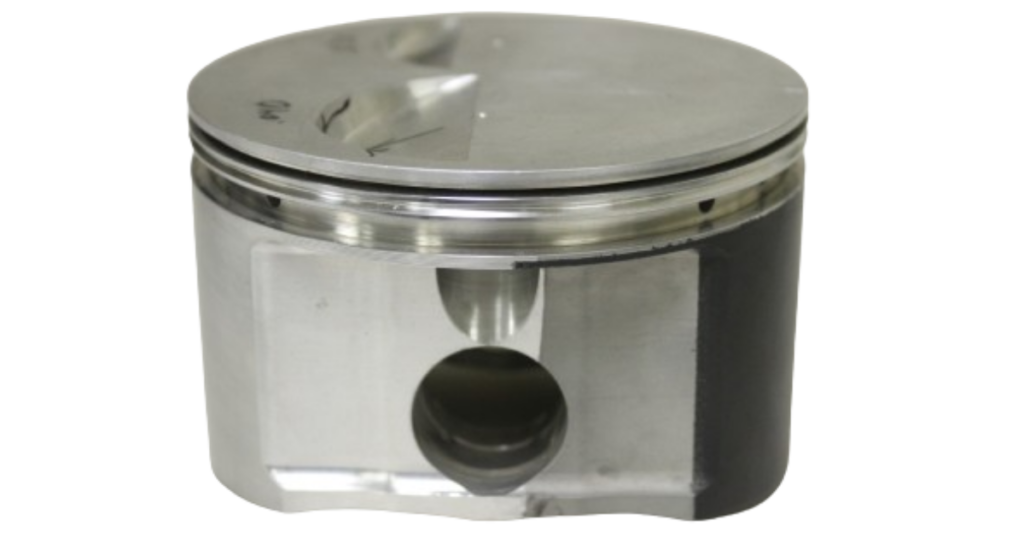

The part of the piston below the crown is called the skirt. This important component not only ensures stability within the cylinder and proper alignment but also plays a vital role in guiding the piston along the cylinder wall. Furthermore, the skirt helps with efficient heat dissipation. Different design choices, like full-round, slipper, or barrel skirts, are used to improve these functions and make the piston work better in the engine.
Piston Rings
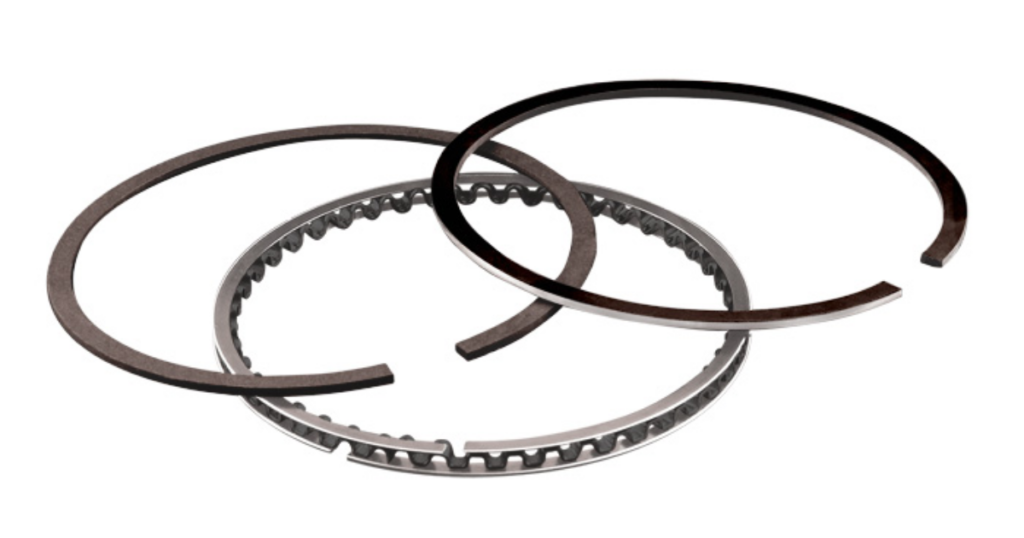

Piston rings create a tight seal between the piston and the cylinder wall. These rings encircle the piston body and are essential for preventing gas leaks and maximizing energy transfer in the engine. There are three types of rings in engines: compression, oil control, and wiper. The rings have multiple functions: sealing combustion gases, controlling oil, and cleaning the cylinder wall. These rings enhance the engine’s performance and durability.
Ring Grooves
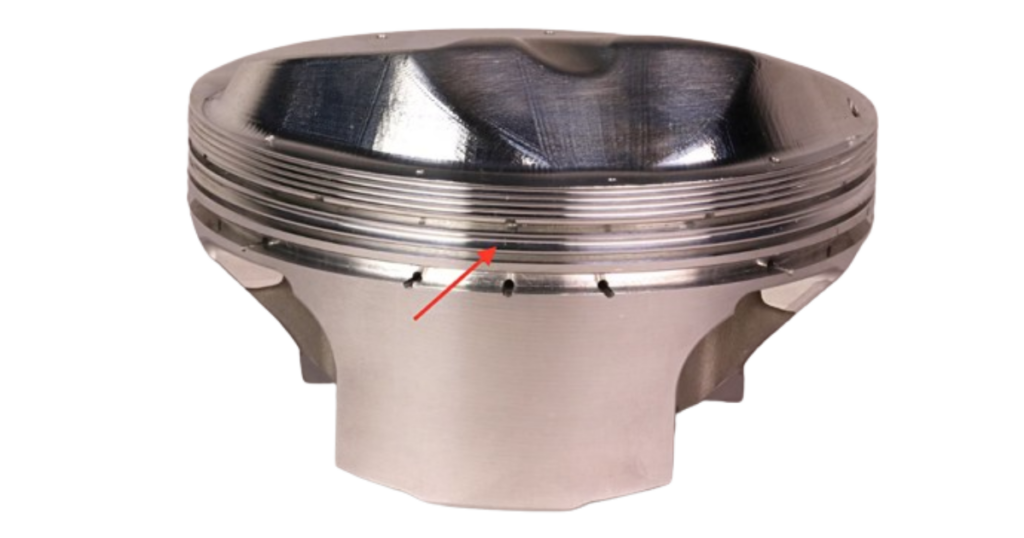

The piston has machined channels called ring grooves that provide stable positions for the piston rings. The grooves hold the rings in place as the piston moves in the engine. To enhance durability and reduce friction, ring grooves can be treated with special coatings or made from materials that are resistant to wear and heat. Implementing these measures can improve the piston assembly’s efficiency and lifespan.
Wrist Pin (Piston Pin)
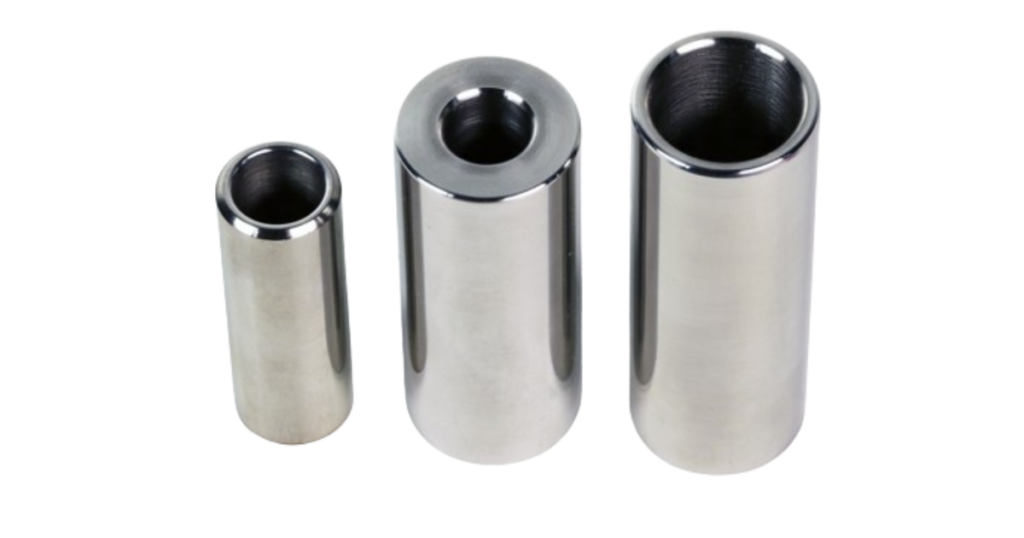

The wrist pin, also known as the piston pin, is crucial as it connects the piston to the connecting rod. It acts as the pivot point for the piston’s oscillating motion inside the engine. Wrist pins are usually made from strong materials, like alloy steel, to handle the powerful forces and loads they experience. This ensures that the engine assembly remains durable and reliable.
Connecting Rod End
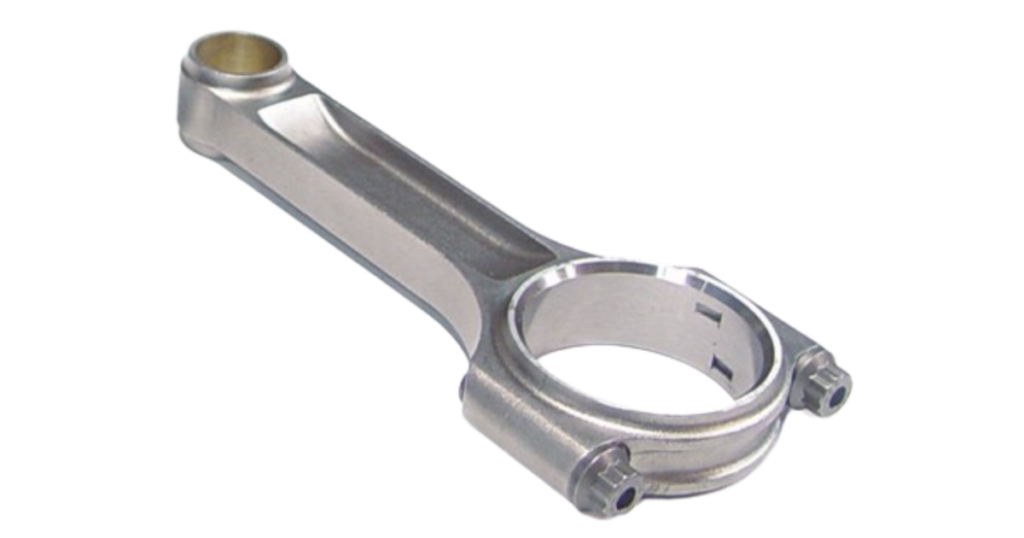

The lower section of the connecting rod is tightly connected to the wrist pin, forming a crucial link that converts the piston’s vertical motion into the rotational motion of the crankshaft in the engine. There are different designs available for the connecting rod end to meet specific engine requirements and load considerations. This design approach ensures excellent performance and durability to meet the unique needs of different engine setups.
Gudgeon Pin (Wrist Pin Retainer)
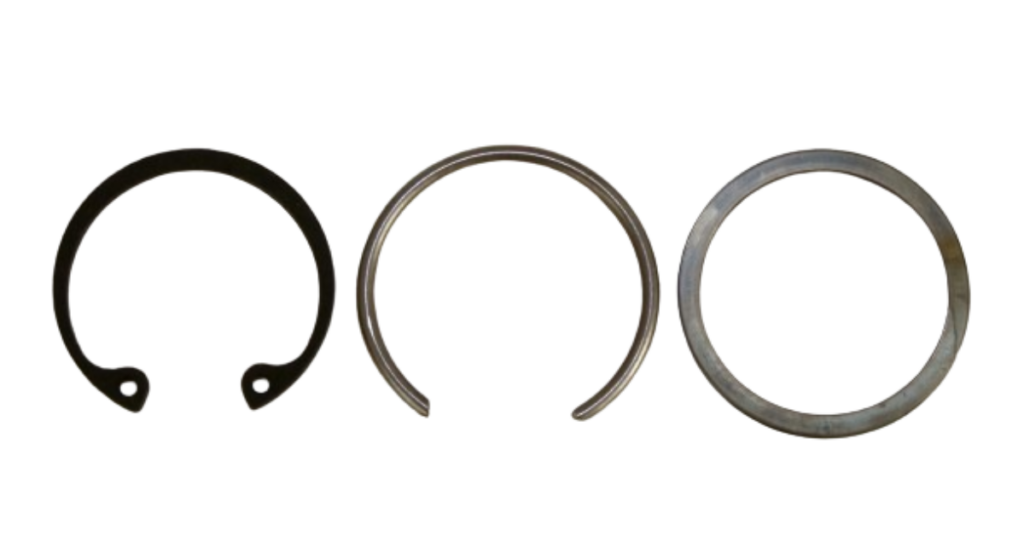

The gudgeon pin, also known as the wrist pin retainer, is essential for securing the wrist pin in the piston. It guarantees the wrist pin’s stability and prevents any lateral movement during engine operation. The gudgeon pin, typically secured with circlips or snap rings, is essential for maintaining a strong connection, preventing accidental disassembly, and improving the stability and reliability of the piston assembly.
Conclusion
While pistons may appear as simple cylindrical components within an engine, the intricacy of their design and the interplay of various parts underscore the remarkable engineering required to harness the power of internal combustion. From the crown and skirt to the piston rings and connecting rod, each element plays a vital role in ensuring efficient energy conversion and optimal engine performance.
As automotive technology continues to evolve, so too will innovations in piston design, pushing the boundaries of efficiency, durability, and power within the engines that drive our modern world.