Sensors are an essential component in the complex world of modern automobiles, as they play a crucial role in ensuring the highest levels of performance, safety, and efficiency. These sensors act as the eyes and ears of your car, communicating information to the engine control unit (ECU) to make modifications in real-time. They are always monitoring and keeping track of their surroundings.
Let’s look into the different types of sensors that can be found in automobiles. Each of these sensors has a distinct role in making sure that the driving experience is both smooth and efficient.
Engine Speed Sensor
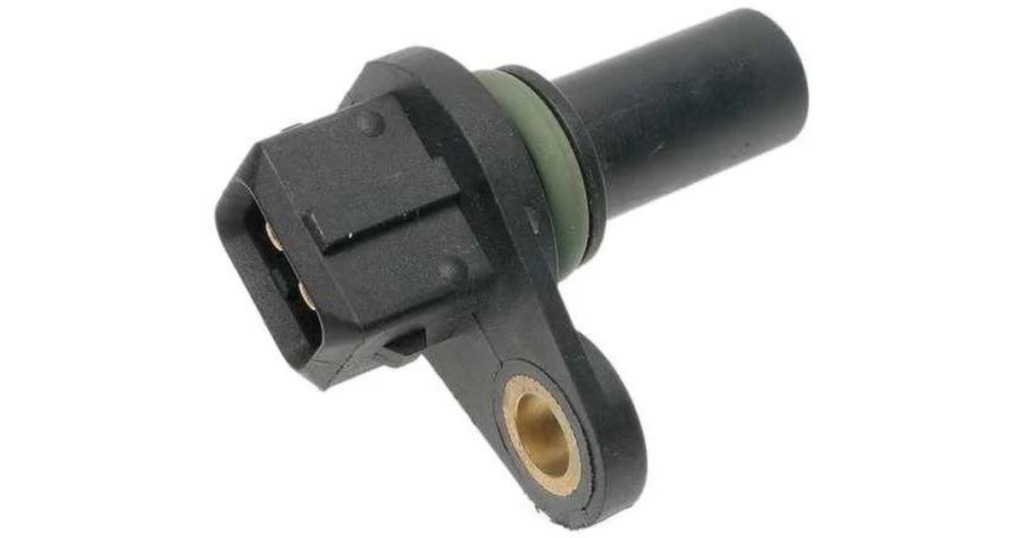

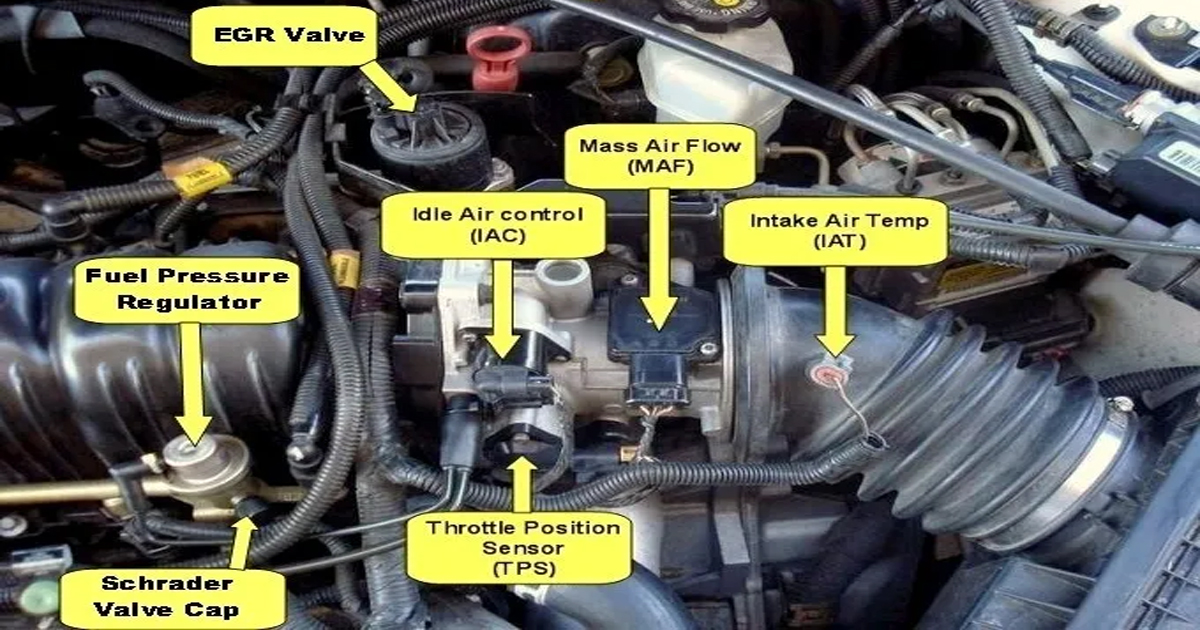
The engine speed sensor, also known as the crankshaft position sensor, monitors the speed at which the engine is rotating. This information is crucial for precise fuel injection and ignition timing, ensuring that the engine operates efficiently and preventing increased emissions or even engine misfires.
Engine Knock Sensor
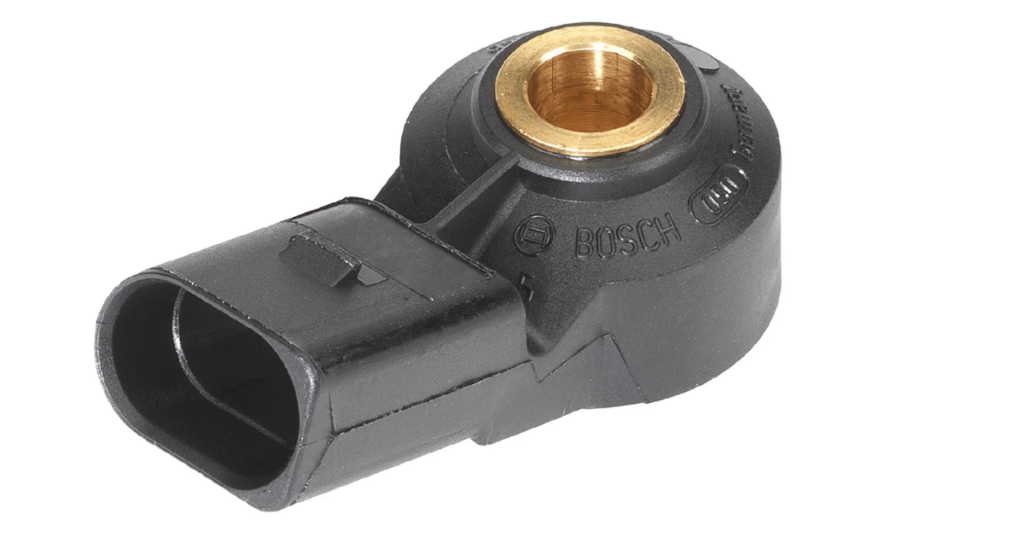

The knock sensor detects abnormal combustion, commonly known as engine knocking. It listens for the characteristic sound produced when fuel ignites unevenly. Once detected, the knock sensor signals the ECU to adjust the ignition timing, preventing potential damage to the engine and optimizing fuel efficiency.
Air Flow Sensor
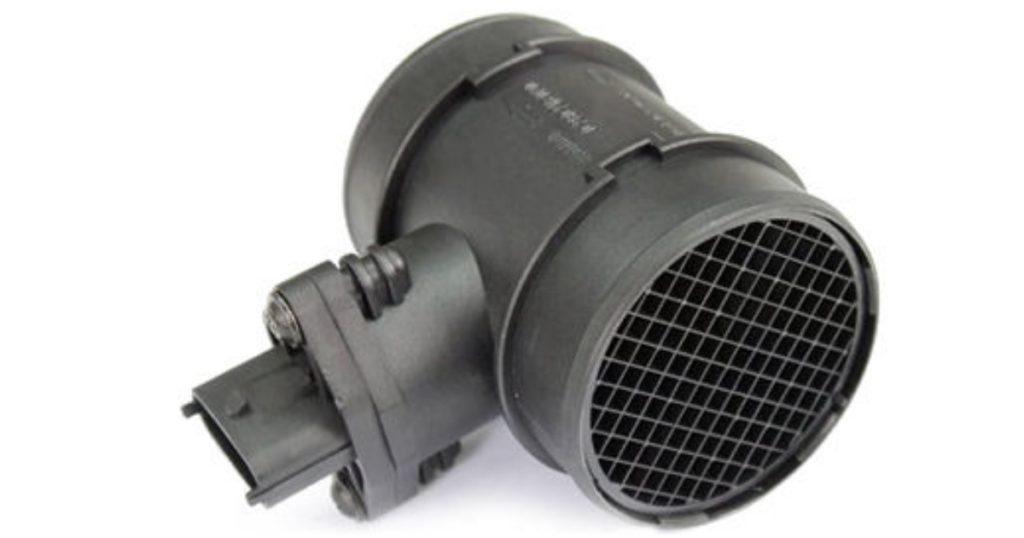

The airflow sensor measures the amount of air entering the engine, allowing the ECU to adjust the fuel injection accordingly. This ensures an optimal air-fuel mixture for combustion, enhancing engine efficiency and reducing emissions.
Cam Sensor
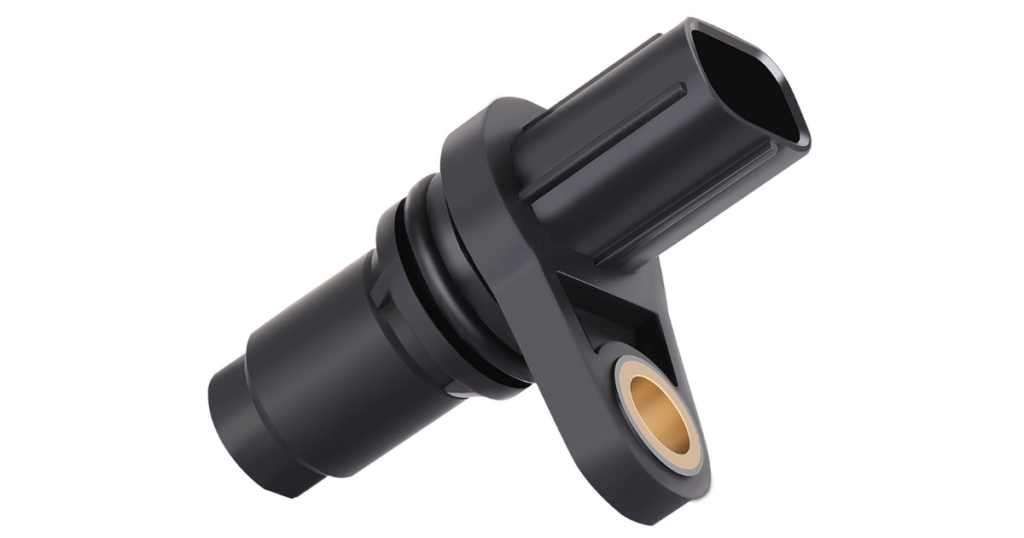

The camshaft position sensor monitors the position of the camshaft, providing essential data for the proper timing of the intake and exhaust valves. Accurate valve timing is crucial for optimal engine performance, and the cam sensor plays a key role in achieving this precision.
Coolant Sensor
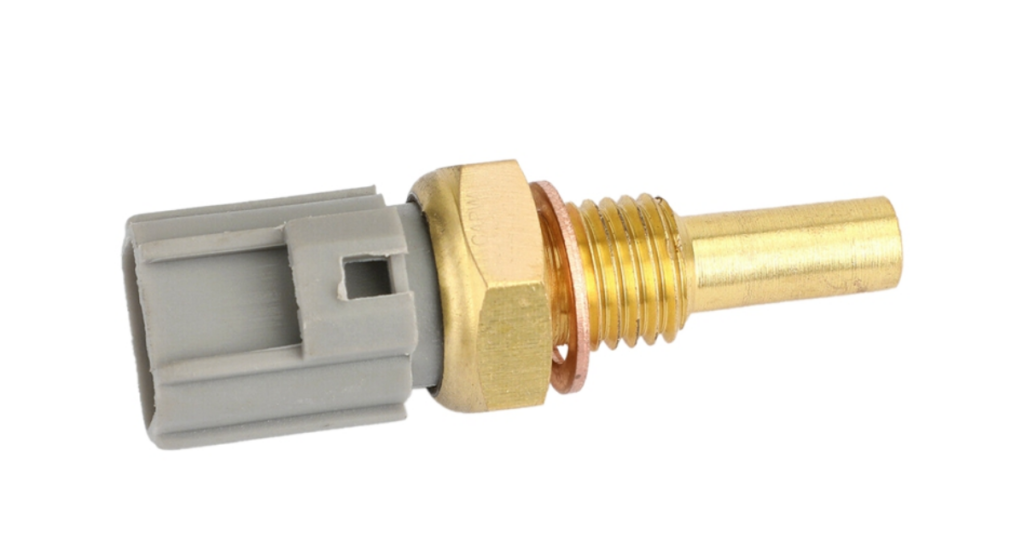
The coolant temperature sensor gauges the temperature of the engine coolant. This information is vital for managing the engine’s operating temperature, preventing overheating, and optimizing fuel combustion.
NOx Sensor
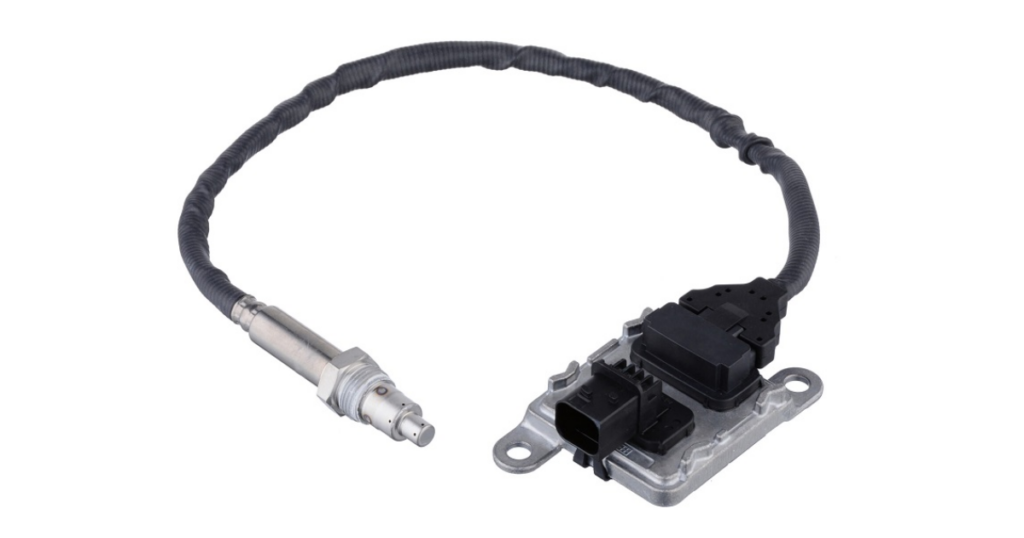

The NOx (nitrogen oxide) sensor is tasked with monitoring and controlling the levels of nitrogen oxides emitted by the vehicle. This is crucial for compliance with emission standards, as excessive NOx emissions contribute to air pollution.
MAP Sensor
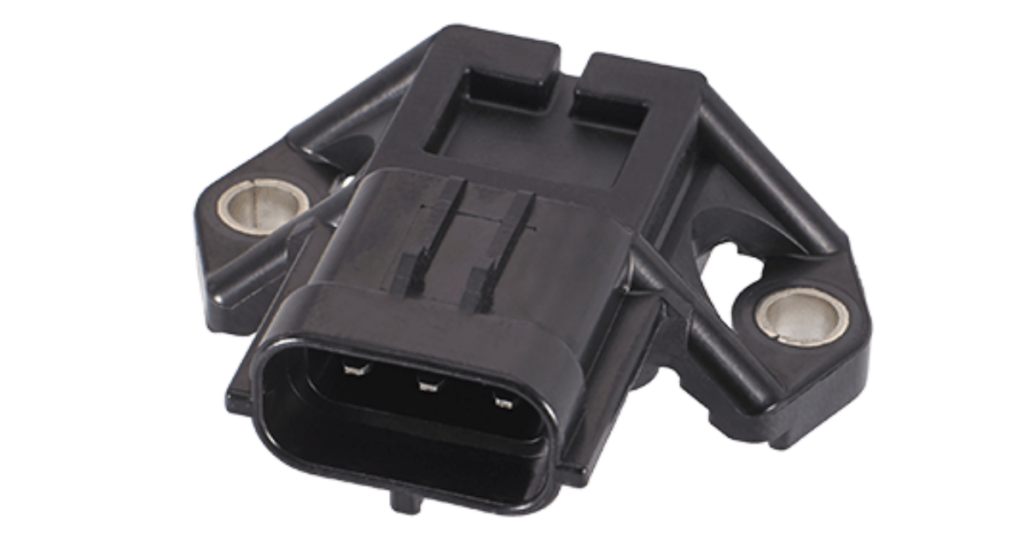

The MAP sensor takes on the role of measuring air pressure in the intake manifold, aiding the ECU in calculating engine load. This information enables the system to fine-tune fuel injection and ignition timing for optimal performance.
Temperature Sensor
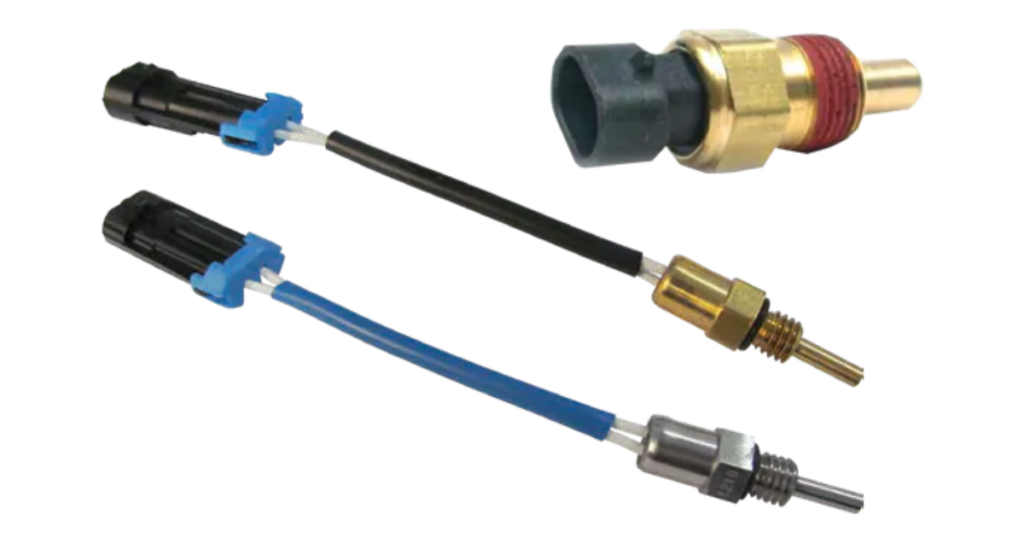

In addition to the coolant sensor, there are various temperature sensors throughout the vehicle. These sensors monitor the temperature of different components, such as the transmission or the intake of air. Proper temperature management is essential for preventing wear and tear and ensuring efficient performance.
Vehicle Speed Sensor
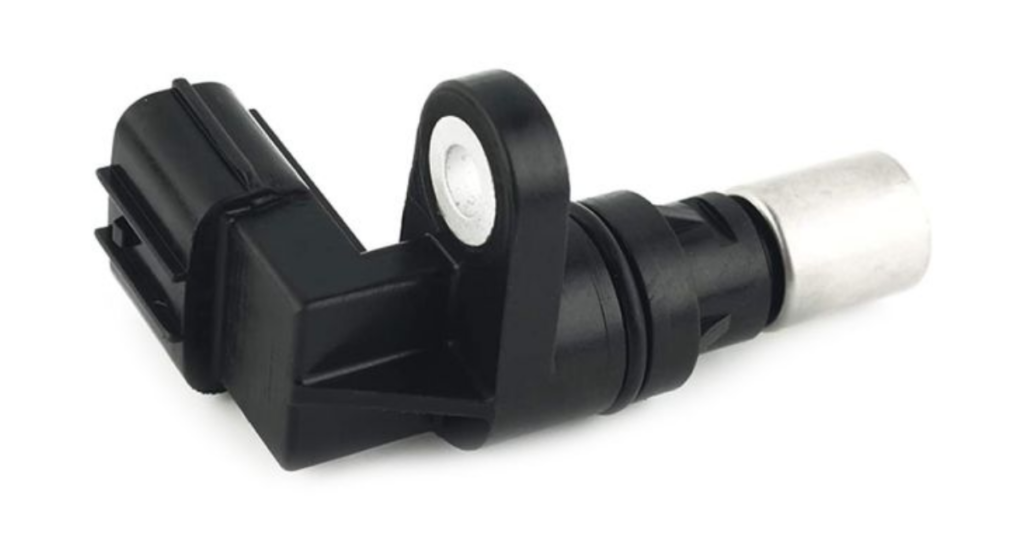

The vehicle speed sensor monitors the speed of the vehicle. This information is crucial for various systems, including the anti-lock braking system (ABS) and the transmission control module, ensuring smooth operation and safety.
Oxygen Sensor
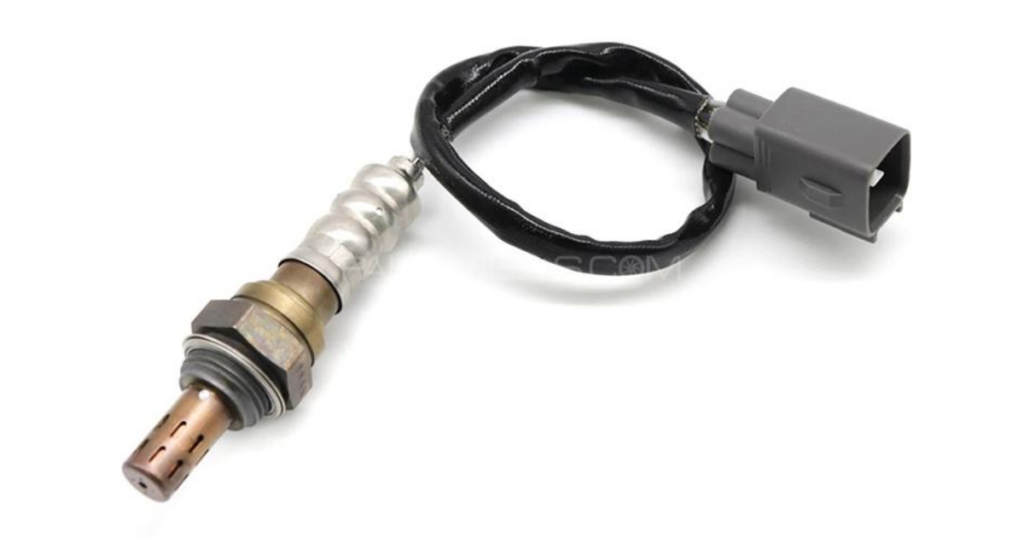

The oxygen sensor measures the level of oxygen in the exhaust gases, providing feedback to the ECU for adjusting the air-fuel mixture. This helps optimize fuel efficiency and reduce emissions.
Throttle Sensor
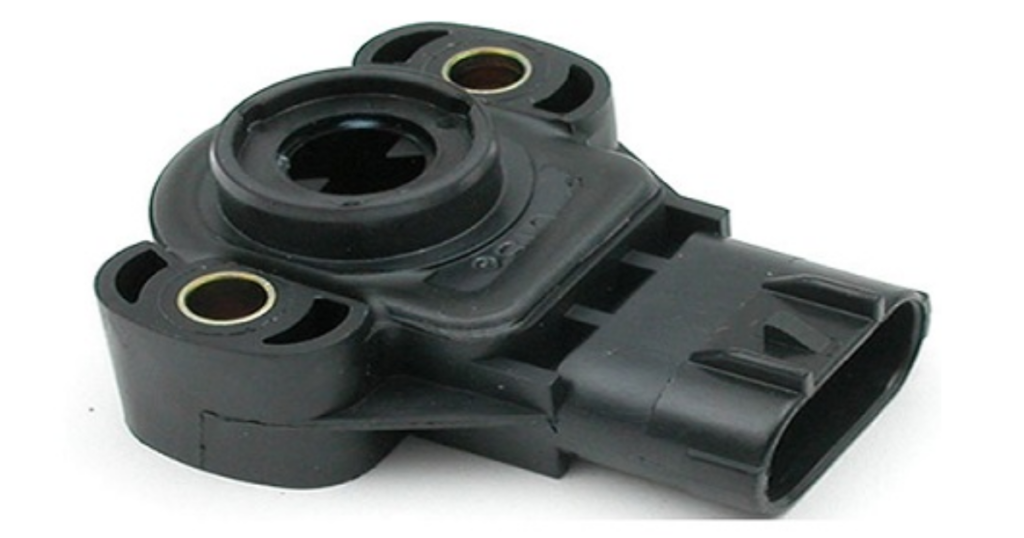

The throttle position sensor monitors the position of the throttle valve, informing the ECU about the driver’s input. This information is essential for adjusting the air-fuel mixture and ensuring smooth acceleration.
Crank Sensor
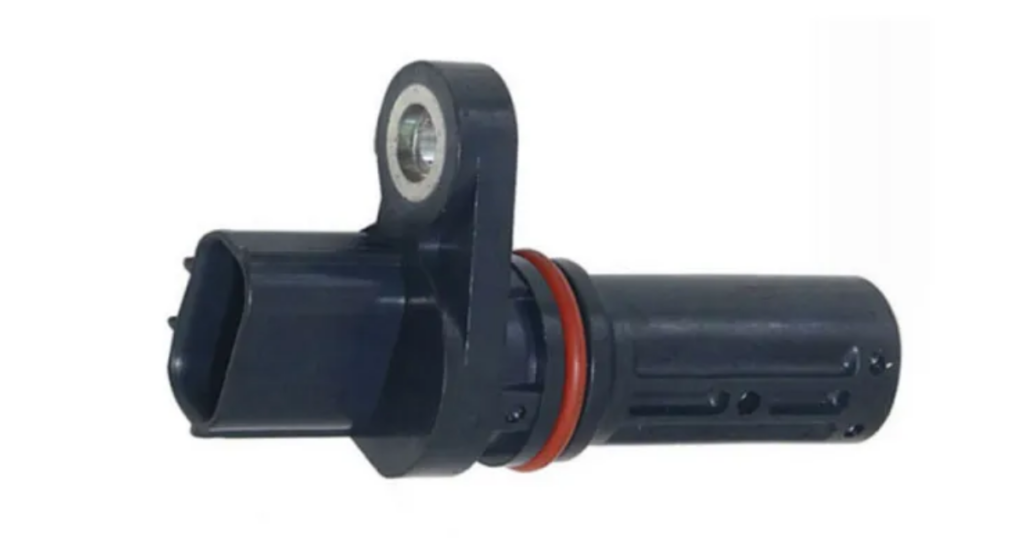

Similar to the cam sensor, the crankshaft position sensor, or crank sensor, provides information about the crankshaft’s position. This data is crucial for accurate ignition timing and fuel injection.
Voltage Sensor
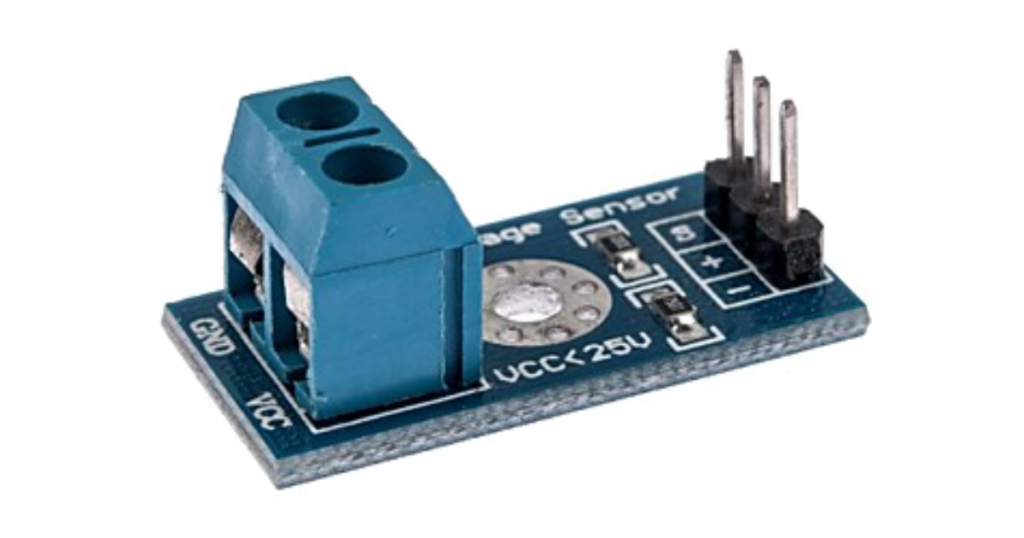
Voltage sensors monitor the electrical voltage within the vehicle’s system, ensuring a stable power supply. They play a vital role in preventing electrical malfunctions and protecting sensitive electronic components.
Rain Sensor
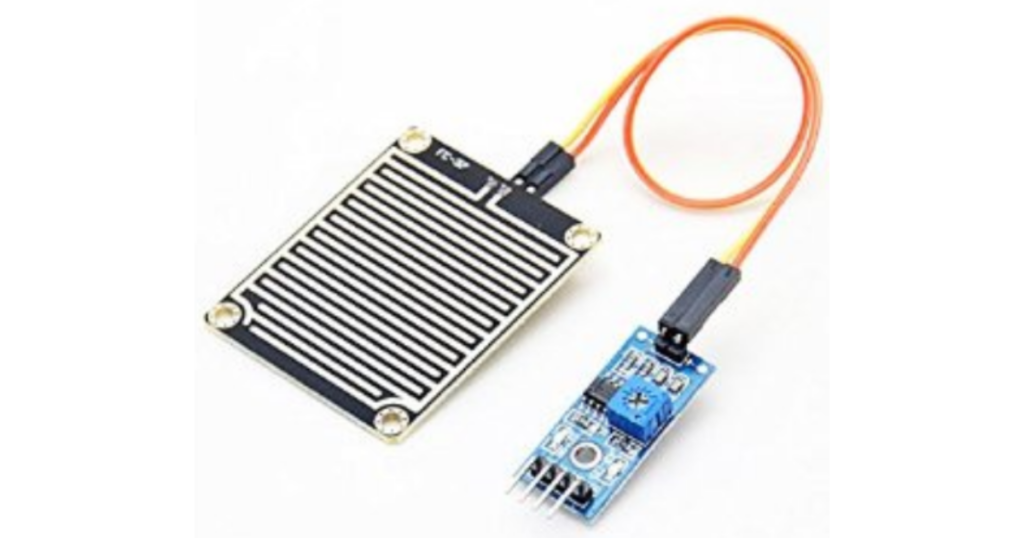

Rain sensors automatically detect rainfall and control the windshield wiper’s speed. This technology enhances driver visibility and safety during inclement weather.
GPS Sensor
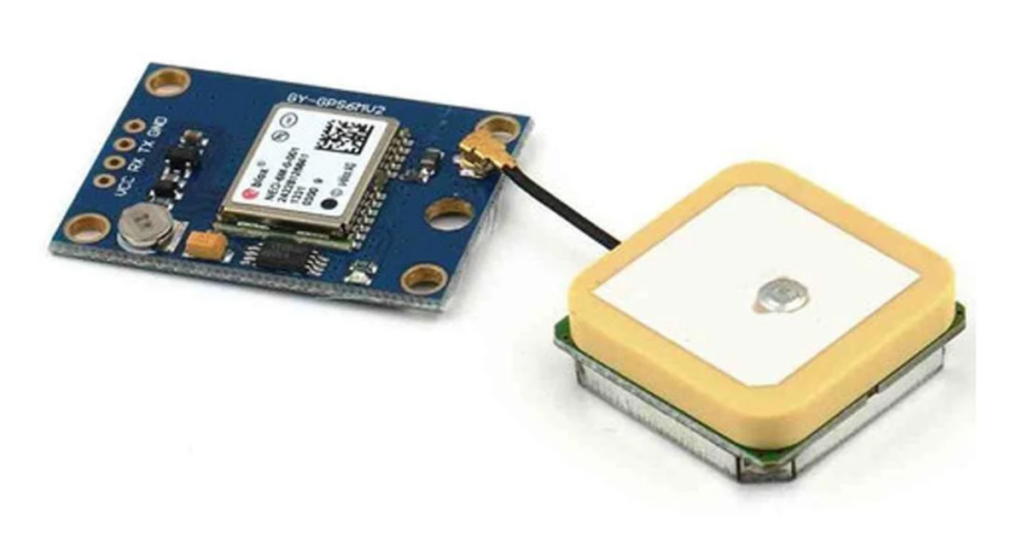

The GPS sensor takes center stage in the navigation ensemble, providing real-time location data. This information not only facilitates precise navigation but also contributes to features like route optimization, tracking, and geofencing.
Conclusion
Automobiles of today have an amazing technological network of sensors that work together to create a correlation of data that improves efficiency, safety, and performance.
Every sensor contributes differently to the smooth running of the car, from keeping an eye on the health of the engine to helping drivers in difficult parking situations. These sensors’ accuracy and real-time modifications allow for better fuel combustion, lower emissions, and a more comfortable ride overall.
Sensors are the silent but obedient guardians of automotive innovation, continuously raising the bar for modern driving.
For a more detailed video explanation and enhanced visuals, please take a look at the video below.