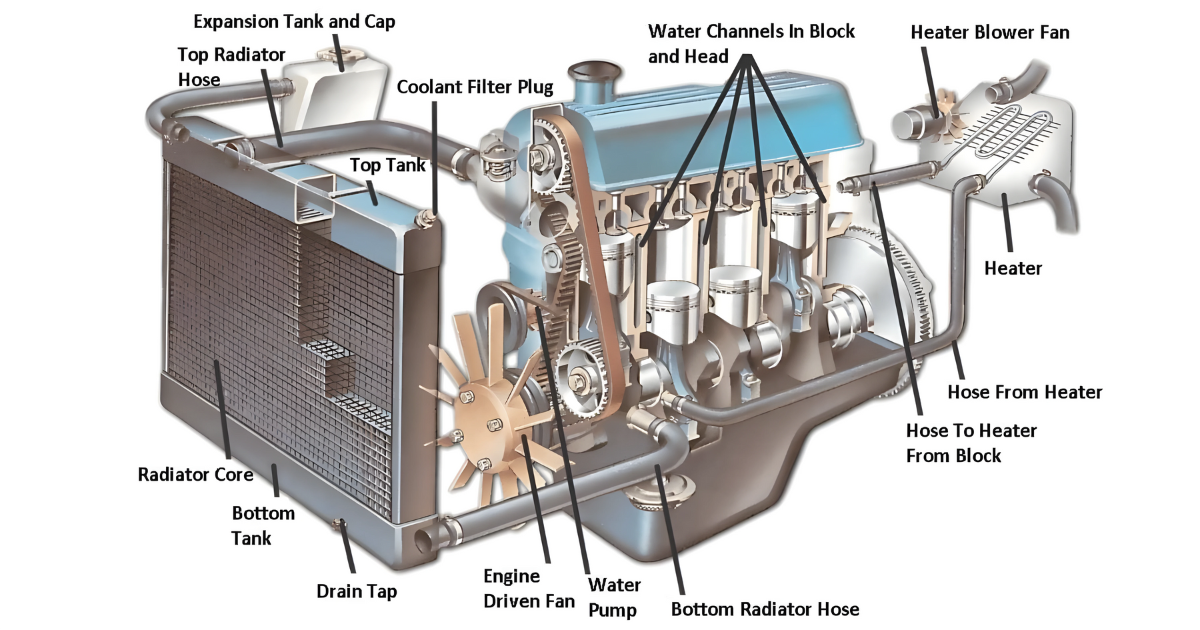
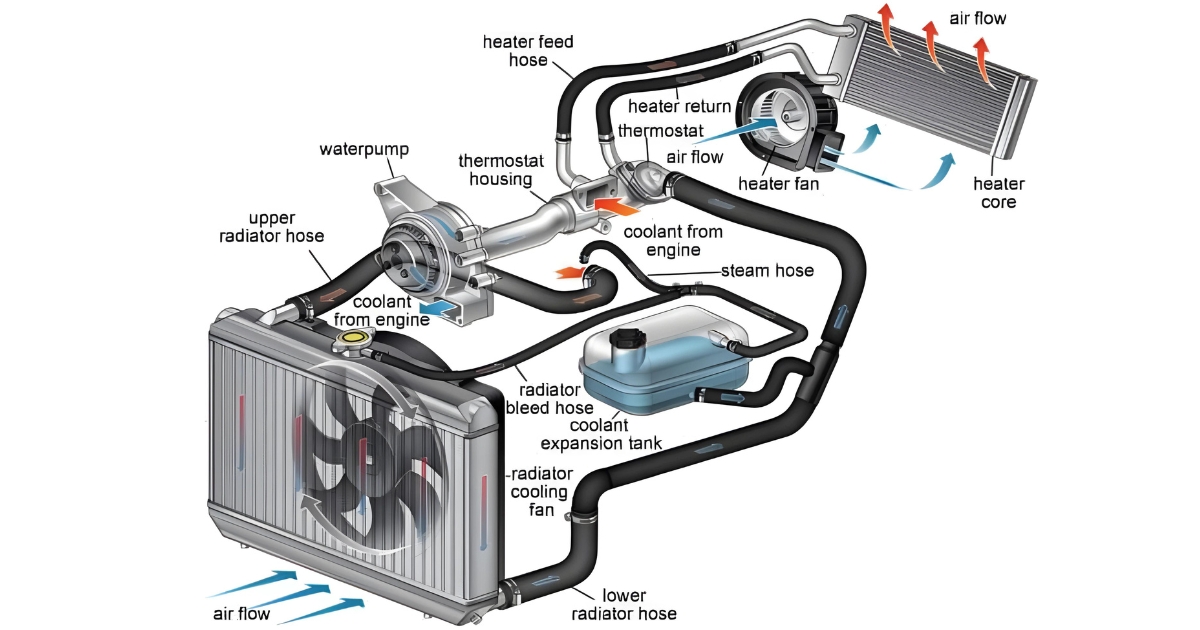
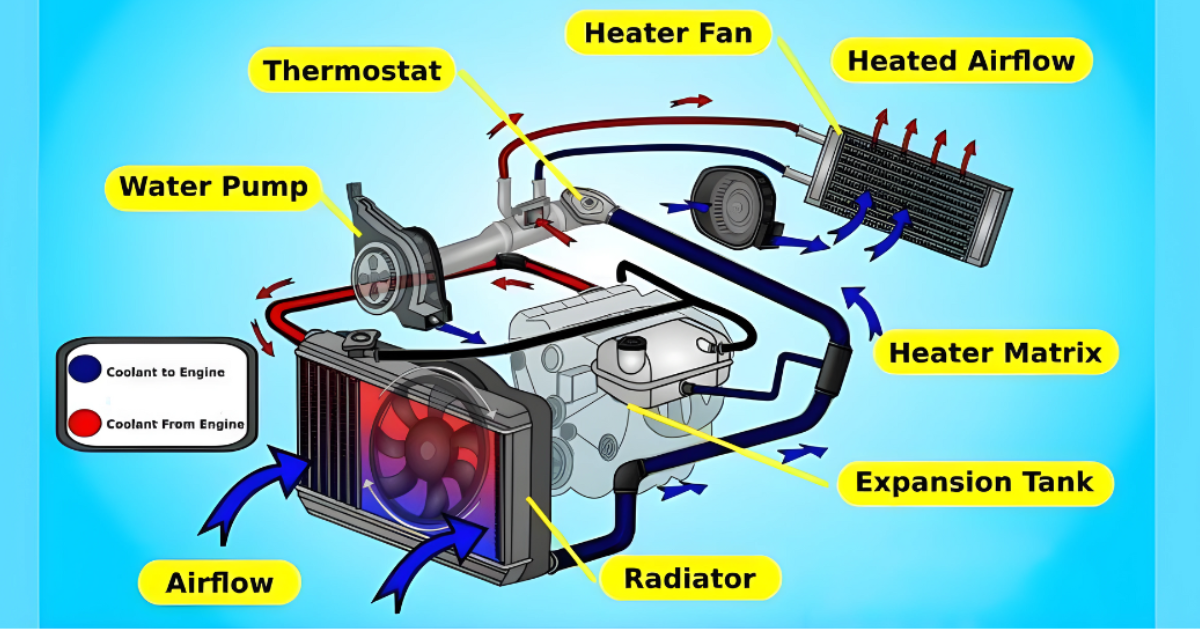
In the world of advanced machinery and electronics, it is crucial to maintain the right temperatures for long-lasting performance and efficiency. When it comes to cooling systems, water cooling has become a more advanced solution that surpasses traditional methods.
Let’s go through the fascinating world of water cooling systems, exploring the different types that meet the needs of modern technology.
Closed-Loop (All-in-One) Water Cooling Systems
Closed-loop water cooling systems, often referred to as all-in-one (AIO) coolers, are compact and user-friendly solutions designed for easy installation. These systems come pre-assembled, featuring a closed loop where the coolant circulates through a pump, tubing, and a radiator with integrated fans.
Components
- Pump: The pump is responsible for circulating the coolant through the closed loop, maintaining a steady flow.
- Radiator: A radiator, equipped with fans, dissipates heat from the coolant as it passes through, ensuring efficient cooling.
- Tubing: Durable and flexible tubing connects the components of the closed loop, facilitating the flow of coolant.
Custom (Open-Loop) Water Cooling Systems
Custom water cooling systems offer enthusiasts and professionals the freedom to design a cooling solution tailored to their specific needs. Unlike closed-loop systems, custom setups involve individually selected components, providing greater flexibility and performance customization.
Components
- CPU/GPU Water Blocks: These specialized blocks make direct contact with the CPU or GPU, transferring heat to the coolant.
- Reservoir: The reservoir holds the coolant and may include features like a pump top or additional ports for customization.
- Pump: The pump is a vital component in custom loops, ensuring efficient coolant circulation.
- Tubing: Users can choose tubing based on aesthetics and performance preferences, with various materials and sizes available.
- Radiator: Custom systems can feature radiators with different sizes and thicknesses, optimizing heat dissipation.
- Fittings: Fittings connect various components, and their design impacts the aesthetics and functionality of the loop.
Passive Water Cooling Systems
Passive water cooling systems take a silent and energy-efficient approach by eliminating the need for active fans. These systems leverage natural convection and radiators to dissipate heat without relying on mechanical components.
Components
- Heat Exchanger/Radiator: Passive systems feature larger radiators with extended surface areas to enhance heat dissipation.
- Reservoir: The reservoir stores the coolant, and the natural convection process facilitates the movement of the coolant through the system.
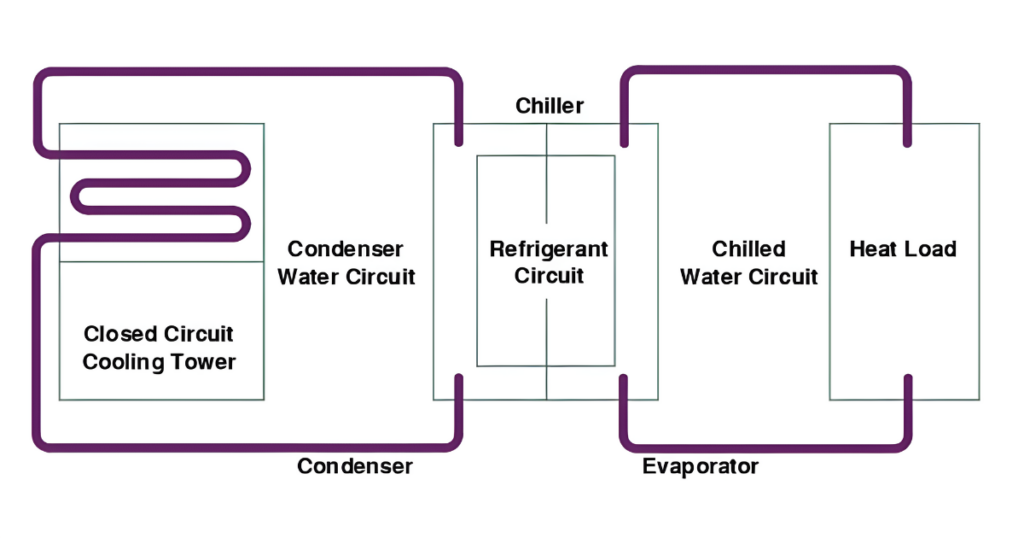
Chilled Water Cooling Systems
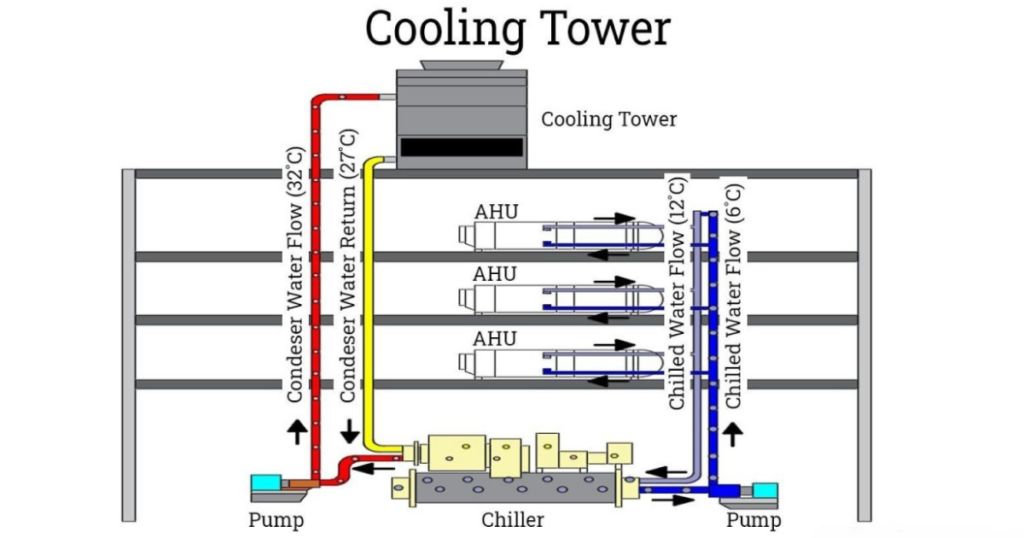
Chilled water cooling systems take a unique approach by using a separate chiller unit to lower the temperature of the water before circulating it through the cooling loop. This allows for precise temperature control and is commonly used in industrial applications and data centers.
Components
- Chiller Unit: The chiller unit is responsible for cooling the water to a set temperature before it enters the cooling loop.
- Cooling Loop Components: Similar to custom water cooling loops, chilled water systems include water blocks, tubing, radiators, and pumps.
Conclusion
Water cooling systems are one of the most advanced and efficient choices available today for a wide range of cooling requirements. Different types of cooling systems have different advantages. Closed-loop AIO coolers are simple; open-loop configurations allow for customization; passive systems operate silently; and chilled water systems provide precise cooling.
Water cooling systems are still the best thermal management solution since they keep high-performance devices cool, quiet, and controllable even when subjected to extreme heat or cold.
For a 3D animated explanation of how an engine cooling water system works, take a look at the video below.