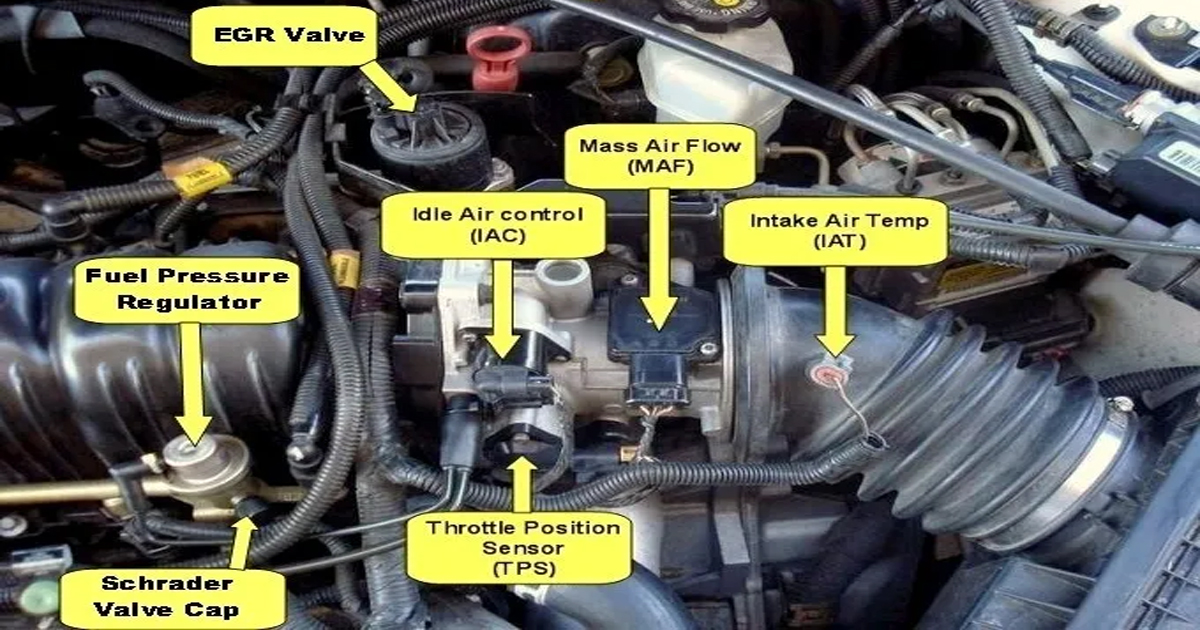
Navigating the world of car sensors can be like trying to understand a foreign language. But fear not! We’re here to turn those baffling abbreviations into clear, actionable knowledge. Get ready to become a pro at understanding the vital sensors that keep your car running smoothly.
A car sensor is an electronic device that monitors various aspects of the vehicle and sends information to the driver or ECU (Electronic Control Unit). Below are abbreviations of the ten common Car Sensors and Their Meaning:
- ACT (Air Charge Temperature) Sensor: A sensor that measures the temperature of the air entering the engine. It helps the engine control unit (ECU) adjust the fuel ratio and ignition timing for optimal performance and efficiency.
- AFM (Air Flow Meter) Sensor: It measures the volume of air flowing into the engine. It is used in older fuel injection systems to determine the correct amount of fuel to inject into the engine.
- APP (Accelerator Pedal Position) Sensor: This sensor measures the position of the accelerator pedal and sends this information to the ECU. The ECU uses this data to adjust the throttle opening and fuel injection rate to match the driver’s demand.
- CAS (Crankshaft Position) Sensor: It measures the crankshaft’s position in relation to the engine’s timing. The ECU uses it to determine the correct timing for fuel injection and ignition.
- CPS (Camshaft Position) Sensor: This sensor measures the position of the camshaft in relation to the engine’s timing. The ECU uses it to determine the correct timing for fuel injection and ignition.
- CTS (Coolant Temperature) Sensor: Monitors the temperature of the coolant that is being pumped around the battery to cool the battery module of EV/PHEVs. The ECU uses it to adjust the fuel ratio, ignition timing, and other engine parameters based on the operating temperature.
- ECT (Engine Coolant Temperature) Sensor: This sensor measures the temperature of the engine coolant. The ECU uses it to adjust the fuel ratio, ignition timing, and other engine parameters based on the engine’s operating temperature.
- EGO (Exhaust Gas Oxygen) Sensor: This sensor measures the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gas. It is used by the ECU to adjust the fuel ratio for optimal performance and fuel efficiency.
- IAT (Intake Air Temperature) Sensor: This sensor measures the temperature of the air entering the engine. It is used by the ECU to adjust the fuel ratio and ignition timing based on the temperature of the incoming air.
- MAT (Manifold Air Temperature) Sensor: This sensor measures the temperature of the air inside the intake manifold. The ECU uses it to adjust the fuel ratio and ignition timing based on the temperature of the air in the manifold.