Underneath every vehicle, concealed within the complex mechanics of wheels and power, is a crucial part that allows for seamless turns and flexible mobility—the Constant Velocity (CV) axle. The CV axle is an important component of the drivetrain. It helps transfer power from the engine to the wheels while also allowing for the movement of the wheels.
Let’s explore the mechanics of the CV axle, explaining its construction, functions, and important role in modern automotive design.
Understanding the CV Axle
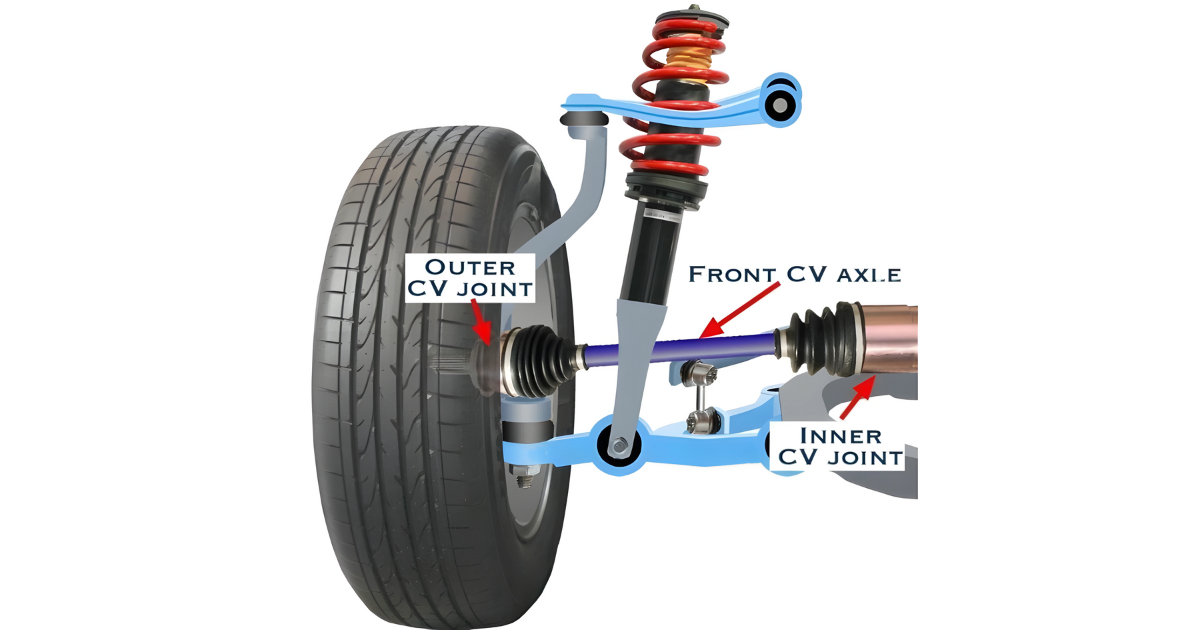
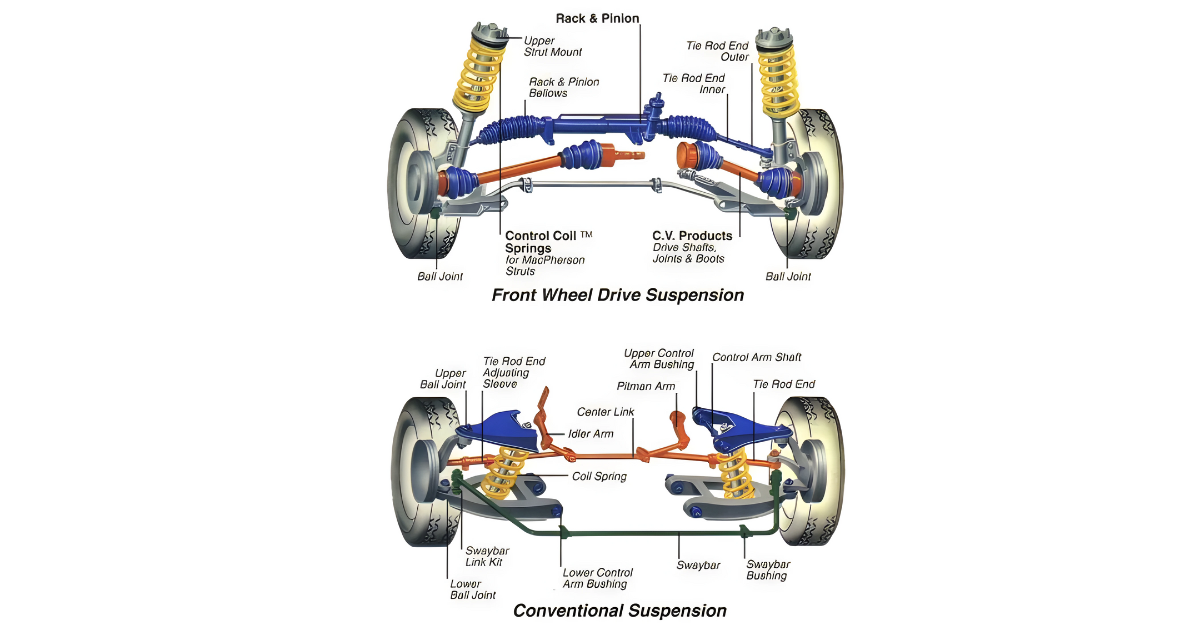
The CV axle, or Constant Velocity axle, serves as a shaft linking the transmission to the wheels, transferring power from the engine while accommodating the vertical movement of the suspension. Predominantly present in front-wheel-drive vehicles, CV axles play a vital role in transmitting power to the front wheels and facilitating steering movements.
Components and Construction
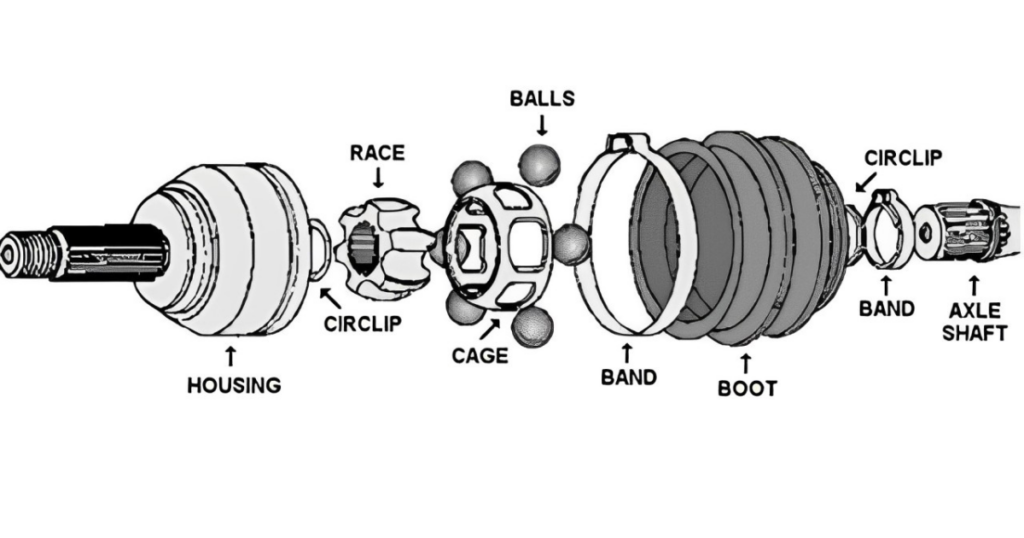
- Axle Shaft: The main shaft of the CV axle, known as the axle shaft, extends from the transmission to the wheel hub. It is responsible for transmitting rotational power to the wheel.
- CV Joints: Constant Velocity joints, or CV joints, are articulated joints located at both ends of the axle shaft. These joints allow for flexibility in the axle, accommodating varying angles and movements.
- Boots and Grease: CV joints are encased in protective rubber boots filled with grease. The boots shield the joints from contaminants and help maintain a lubricated environment, ensuring smooth rotation.
Functionality during Turns
- Steering Movements: During turns, the outer CV joint is subject to angular movements, allowing the axle to change length and accommodate the varying distances between the transmission and the wheel.
- Preventing Binding: The design of CV joints prevents binding, ensuring that power can be efficiently transmitted to the wheels even when they are at different angles.
Inner and Outer CV Joints
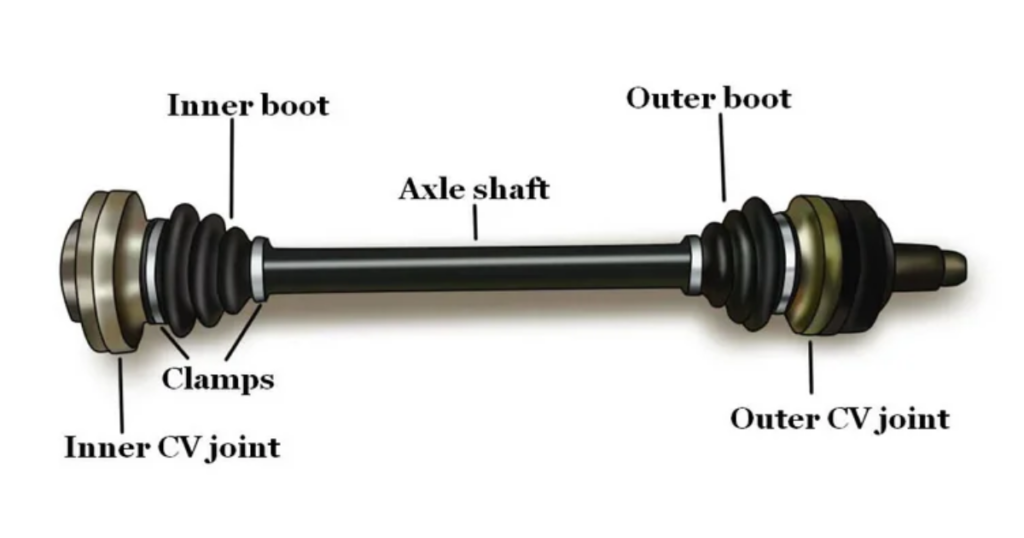
- Inner CV Joint: The inner CV joint connects to the transmission and undergoes more limited movement. It is typically a tripod-style joint that facilitates smooth rotation.
- Outer CV Joint: The outer CV joint, located near the wheel hub, is a ball-and-socket-style joint. This design allows for greater articulation during steering movements.
Issues and Maintenance
- CV Joint Wear: Over time, CV joints can wear out due to constant movement and exposure to the elements. Symptoms of worn CV joints include clicking noises during turns and vibration.
- Boot Damage: Tears or damage to the rubber boots that encase the CV joints can lead to contamination and loss of lubrication. Regular inspection of the boots and timely replacement can prevent damage to the joints.
- CV Axle Replacement: In cases of severe CV joint wear or damage, replacing the entire CV axle assembly is often recommended. This involves removing the old axle and installing a new one, complete with CV joints and boots.
Front-Wheel-Drive and All-Wheel-Drive Vehicles
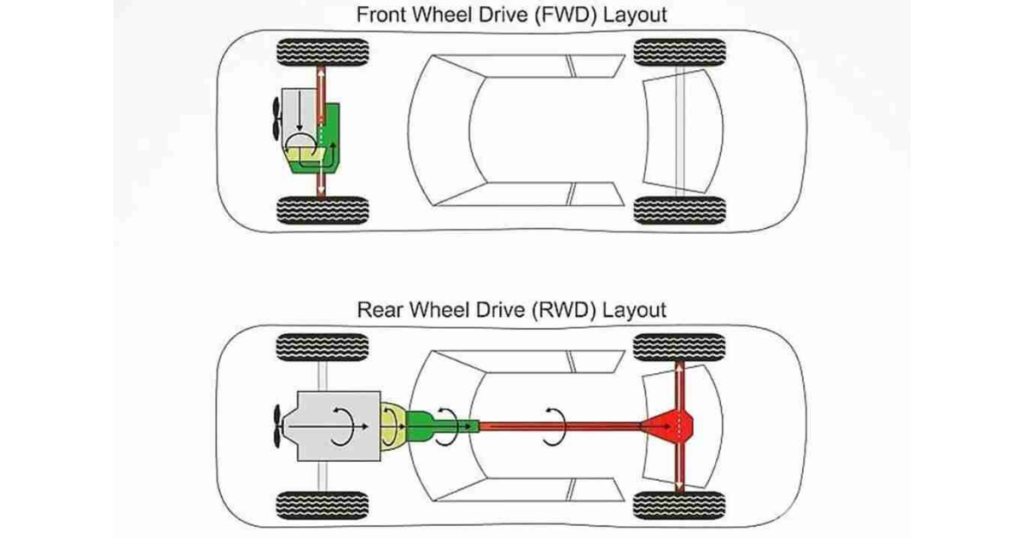
- Front-Wheel-Drive: In front-wheel-drive vehicles, the CV axle is primarily responsible for transmitting power to the front wheels. It undergoes more stress during steering movements.
- All-Wheel-Drive: All-wheel-drive vehicles often have multiple CV axles, serving both front and rear wheels. These axles contribute to the flexibility needed for optimal performance on various terrains.
Advancements in CV Axle Technology
- Improved Materials: Modern CV axles often incorporate advanced materials and manufacturing techniques to enhance durability and reduce weight.
- Electronic Differential Locks: Some advanced systems utilize electronic differential locks, enhancing traction control by selectively applying brakes to specific wheels or adjusting power distribution.
Conclusion
The CV axle, hidden beneath the vehicle’s chassis, embodies the delicate balance between power transmission and flexible movement. As a testament to automotive engineering, the CV axle’s ability to smoothly articulate during turns ensures that every journey is met with efficiency and control. Regular maintenance, including inspections of CV joints and boots, is crucial to prevent issues and extend the lifespan of this unassuming yet vital component.
As we continue to embrace advancements in vehicle dynamics, the constant evolution of CV axle technology promises even greater efficiency and reliability, enabling our vehicles to navigate the twists and turns of the road with grace and precision.
For a visual insight into how a CV axle works to turn your car’s wheels, please take a moment to watch the video below.