Embark on a journey into automotive technology and discover the critical roles of active and passive car sensors. These innovative tools are the unsung heroes, providing safety, convenience, and enhanced driving experiences. Dive into our exploration of these sensors to understand how they work and the ways they revolutionize your daily drives.
There are two kinds of car sensors: active and passive. Although both provide considerable advantages during the rush to and from work or while guiding your car into a parking place, the systems operate differently. Here, we’ll discuss the difference between the two sensors and provide examples for each type of sensor.
What are Active Sensors?
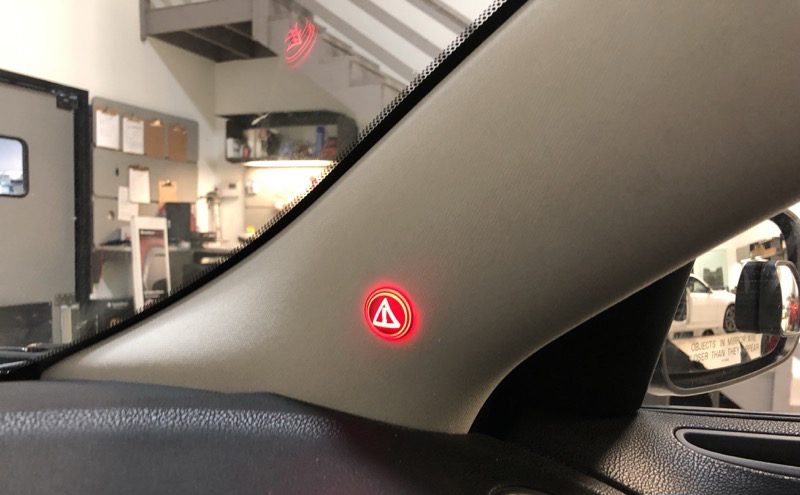

These sensors alert drivers when they are in danger of getting into a crash or sustaining vehicle damage. This warning may be a buzzer, seat or steering wheel vibration, or a flashing light. The driver is not required to take any action to get the alert.
Examples of Active Sensors
Parking sensors and radar-based blind-spot monitoring systems are the two most prevalent active accident prevention sensors. As you approach an item or a person, parking sensors on the bumpers of your car emit an auditory warning. Most installations involve rear sensors.
Radar-based blind-spot monitoring sensors use a pair of microwave transceivers installed at the rear corners of the vehicle to inform the driver when a vehicle is in the car’s blind area. A bright indicator glows when a vehicle enters the parking place next to your vehicle. If you engage your turn signal, the indicator will flash, and a buzzer will alert you of an object in your blind area.
What are Passive Sensors?

These sensors offer the driver vital information without drawing attention to themselves. They detect and respond to some input from the physical environment. Passive sensor technologies gather target data by detecting vibrations, light, radiation, heat, or other phenomena occurring in the subject’s environment.
Examples of Passive Sensors
The most prevalent passive safety sensor is the backup camera. These systems give essential information about nearby items and people. When you pull into your driveway, a parking sensor system will alert you if a bicycle is behind your vehicle.
In contrast, a backup camera does not give any particular warning. The bicycle is visible if you look at the camera. If you do not look, you will hit the bicycle.
Another increasingly common passive warning sensor is a blind-spot camera. Several companies offer these upgrades for trucks and SUVs, and in most cases, the camera image can be displayed on the color screen in the dash. Again, it would be best if you remembered to look at the camera image before changing lanes or turning for these systems to be of benefit.
Which sensors do you think are the most beneficial to you while driving? And which sensors do you wish your car has?