The symphony of a well-functioning engine relies on a meticulous arrangement of components, and at the heart of this mechanical orchestra is the valve mechanism. Understanding the construction of this crucial system is akin to deciphering the engine’s language.
Let’s uncover the inner workings of valve mechanisms, exploring the key parts that work together to coordinate the motion of valves in an engine.
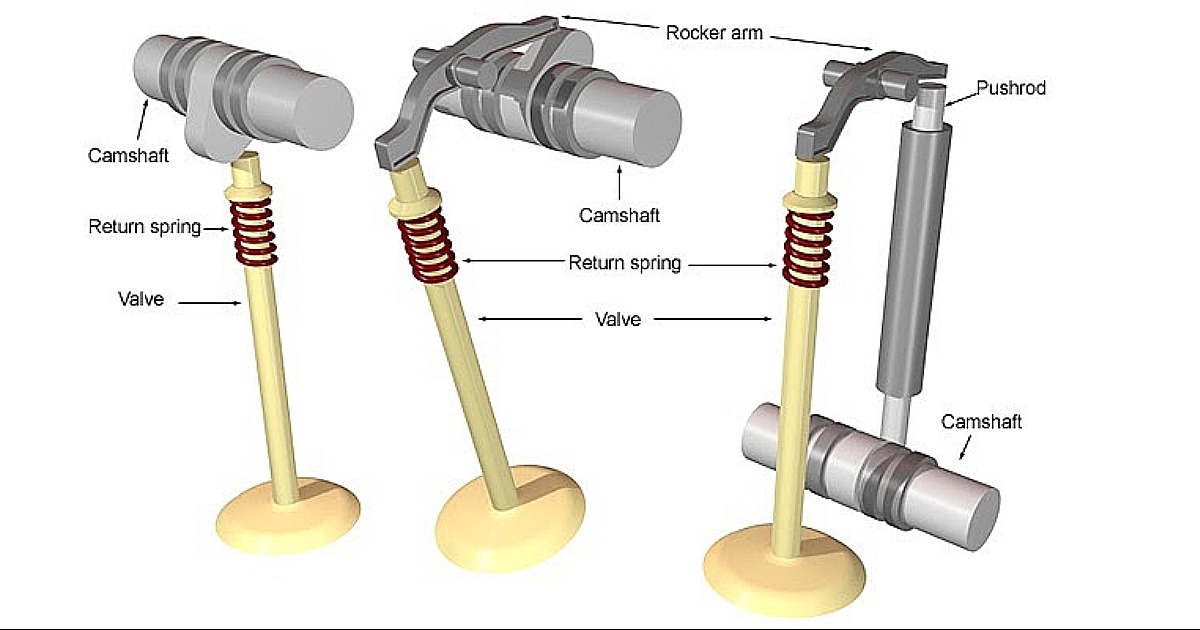
Valves
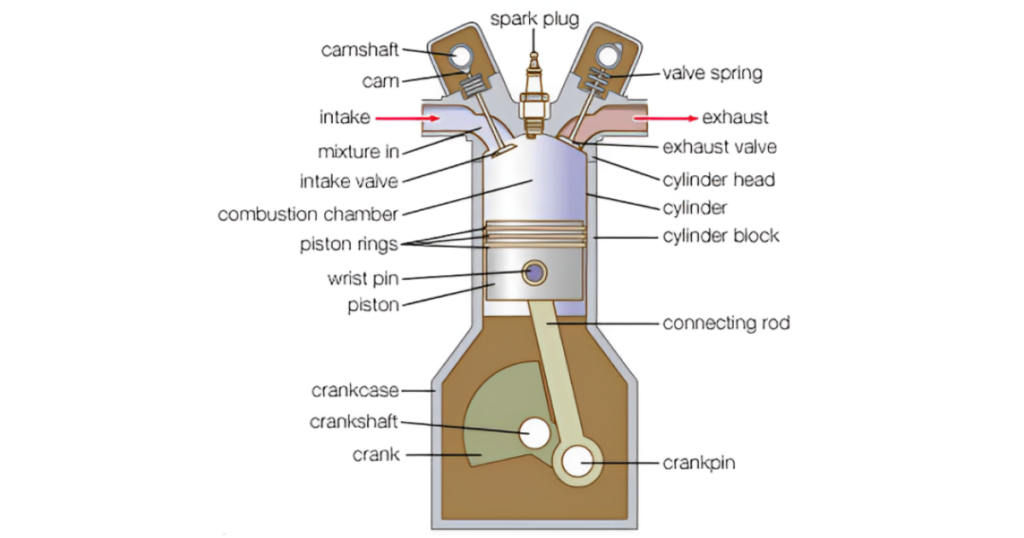
The valves, commonly known as intake and exhaust valves, are the primary actors in the valve mechanism. These are typically made of durable materials like stainless steel and are precision-engineered to withstand the demanding environment within the engine. Valves control the flow of air and exhaust gases in and out of the combustion chamber, playing a pivotal role in the combustion process.
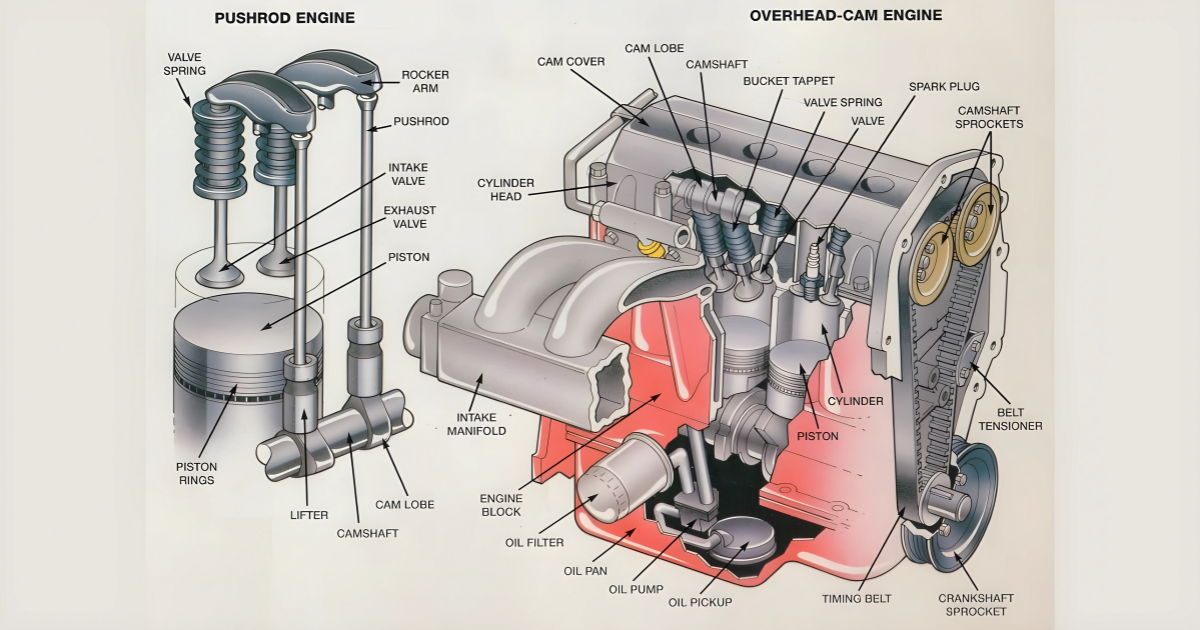
Camshaft
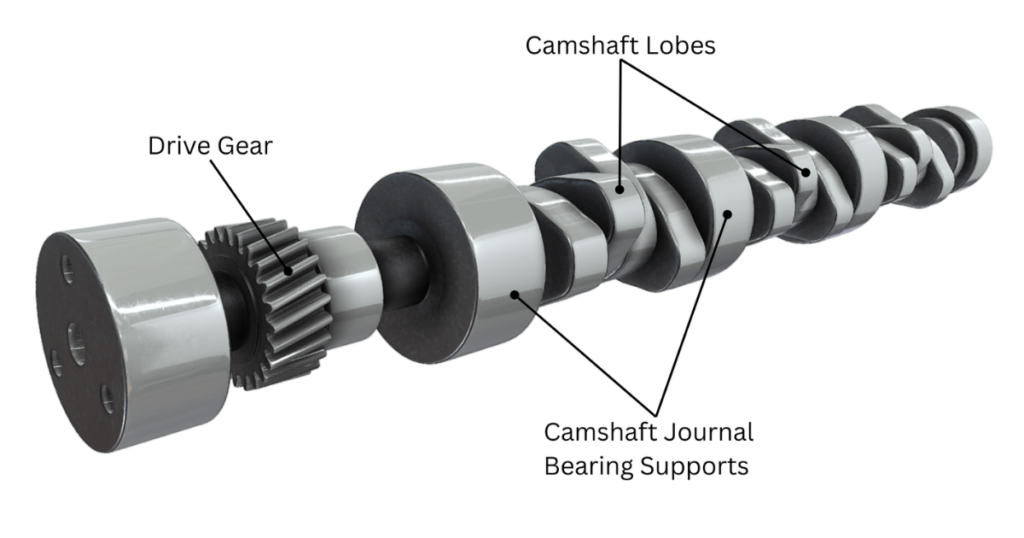
Standing as the central figure in the valve mechanism symphony is the camshaft. This cylindrical shaft, driven by the engine’s crankshaft, houses lobes or cams that determine when the valves open and close. The shape and placement of these lobes on the camshaft are carefully designed to synchronize with the engine’s operation, ensuring optimal performance.
Timing Belt or Chain
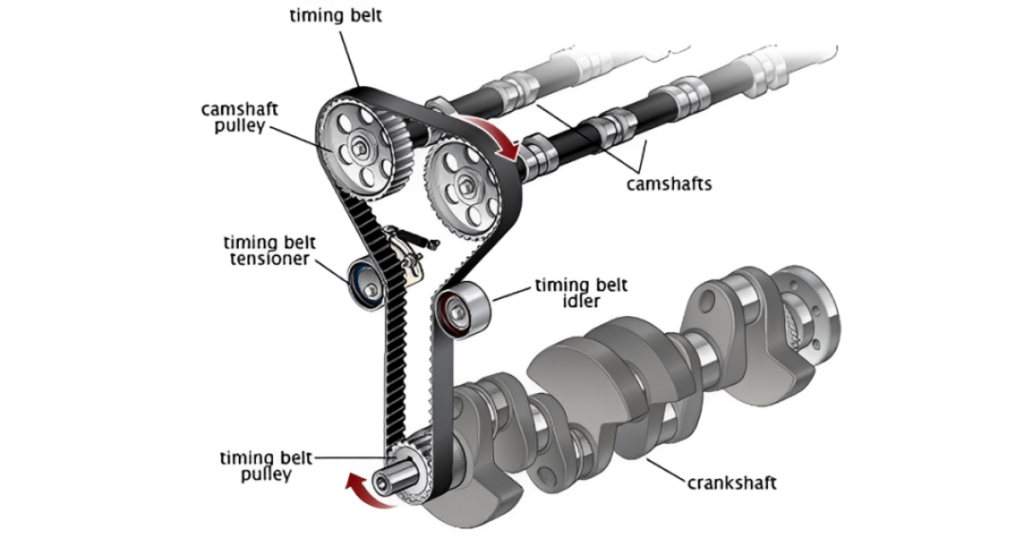
Connecting the crankshaft and the camshaft is the timing belt or chain. This essential component ensures precise timing between the opening and closing of valves and the movement of pistons. A well-maintained timing belt or chain is crucial for preventing misalignment and potential catastrophic engine damage.
Valve Springs
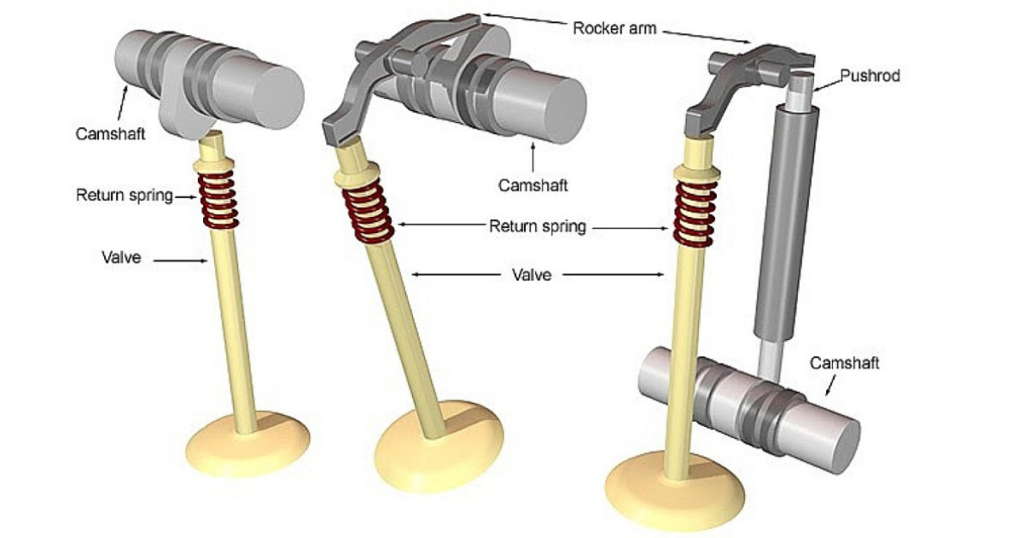
Valve springs play a critical role in the construction of the valve mechanism. They ensure that the valves return to their closed position promptly after opening. These coiled springs undergo significant stress during engine operation, necessitating durability and resilience to maintain their functionality over the engine’s lifespan.
Valve Lifters
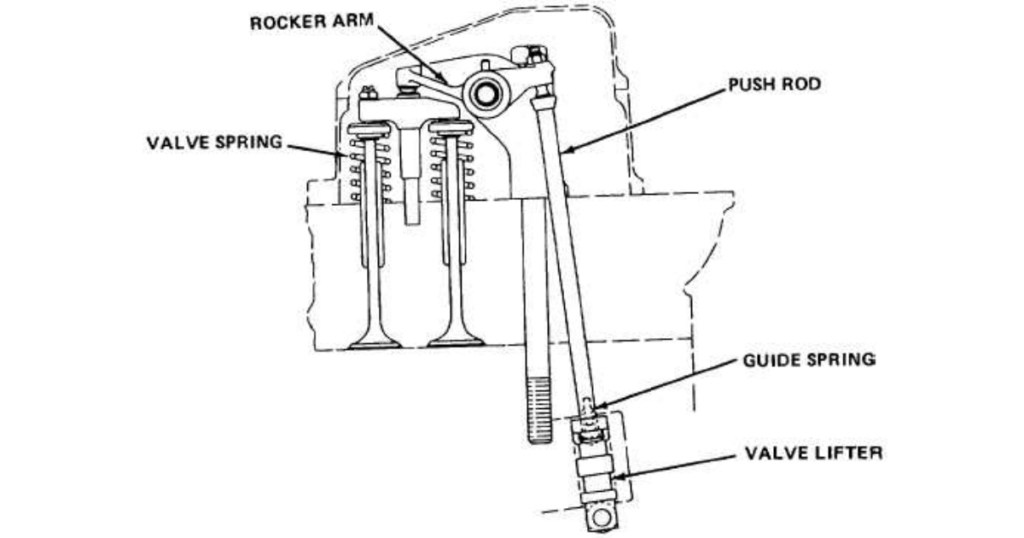
Valve lifters, also known as tappets, are components that transfer the motion from the camshaft to the valves. They move up and down in response to the camshaft’s lobes, providing the necessary lift for the valves to open and close. There are various types of lifters, including hydraulic and mechanical, each contributing to the precision of valve movement.
Pushrods
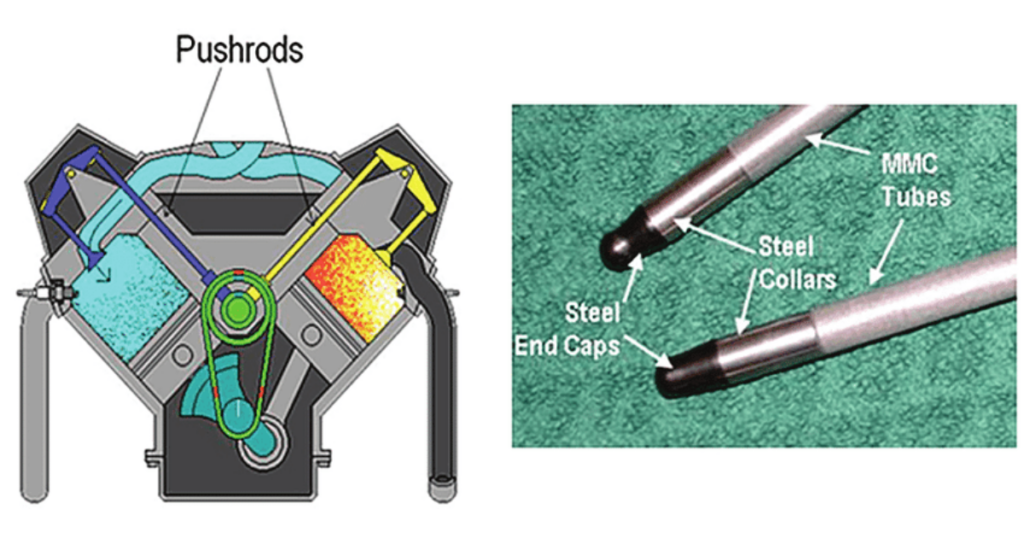
In engines utilizing pushrod systems, these slender rods transmit the motion from the lifters to the rocker arms. The pushrods act as intermediaries, transferring the camshaft’s energy to the valve train’s components and coordinating the delicate dance of the valves.
Rocker Arms
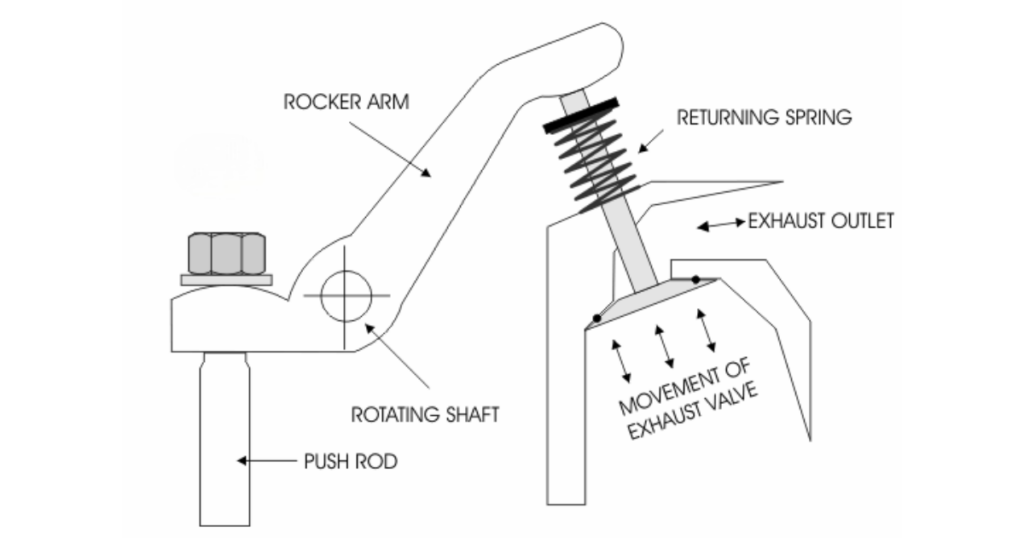
Rocker arms pivot on a fulcrum and transmit the motion from the pushrods to the valves. Rocker arms serve as levers to amplify the lift the camshaft generates, ensuring efficient valve operation. Precision in the design and manufacture of rocker arms is crucial for maintaining valve timing accuracy.
Valve Retainers and Locks
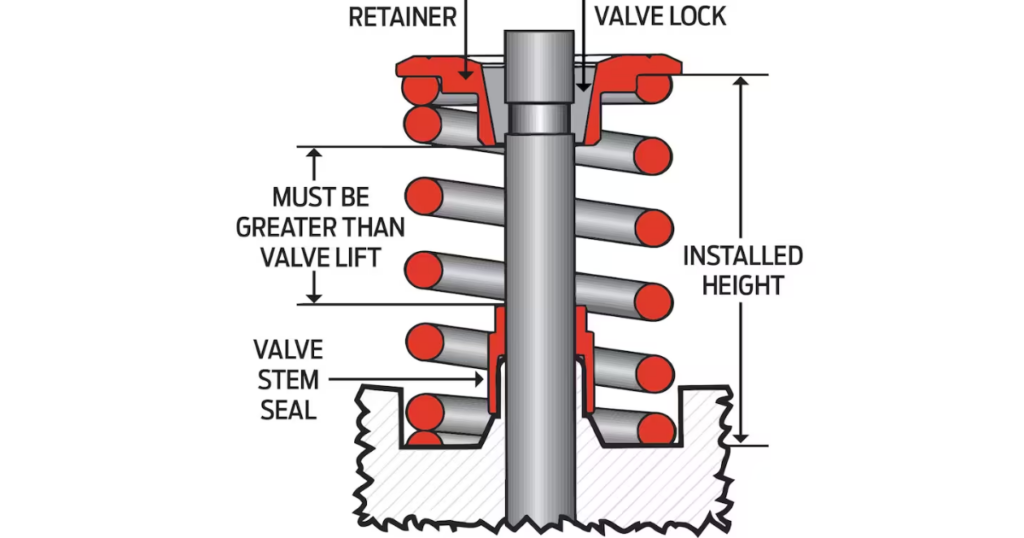
Valve retainers and locks are responsible for keeping the valves in place during the engine’s operation. They prevent the valves from bouncing or fluttering, maintaining stability and preventing potential damage to the valves or other engine components.
Conclusion
The valve mechanism is a wonder of precision engineering in the complex world of engine construction. By breaking down its parts, which include the rocker arms, retainers, lifters, pushrods, camshaft, timing belt or chain, valve springs, and lifters, we can better understand the careful engineering needed to ensure smooth engine operation.
A perfectly functioning valve system ensures that the engine runs, breathes, and fires. Whether you’re a seasoned automotive enthusiast or an aspiring mechanic, appreciating the construction of the valve mechanism provides a deeper understanding of the rhythmic complexities that power our vehicles.