The many fuses and relays found in an automobile’s fuse box are each assigned an acronym that serves as a general indication of their function. Abbreviations such as MG/C, ST, EFI, DIM, HDLP, H-LP, etc. can be found on the inside of your fuse box.
What does HDLP mean in the fuse box?
The HDLP relay fuse is short for “headlight fuse” in most vehicles. When the headlamp gets too hot, it fractures a fusible component to stop the current from passing, protecting it from overcurrent.
The headlight wash fuse is known as an HDLP wash fuse. The current that reaches the system is regulated by an HDLP wash fuse, which is present in vehicles that have automatic headlamp washers. The washing pump is powered by the fuse. The 20A HDLP fuse is usually located in the left engine compartment fuse box on most automobiles.

User reports indicate that the HDLP, which may be labeled HDLP #1 or #2, is a 15-amp fuse that may be found behind the dashboard’s border. The placement and amperage of the HDLP fuse, thus, differ from one vehicle to another. If you want an answer that’s particular to your vehicle, I suggest looking in the handbook for information about the HDLP fuse.
Now that we know what HDLP is, let’s have a look at how it operates.
How does an HDLP fuse work?
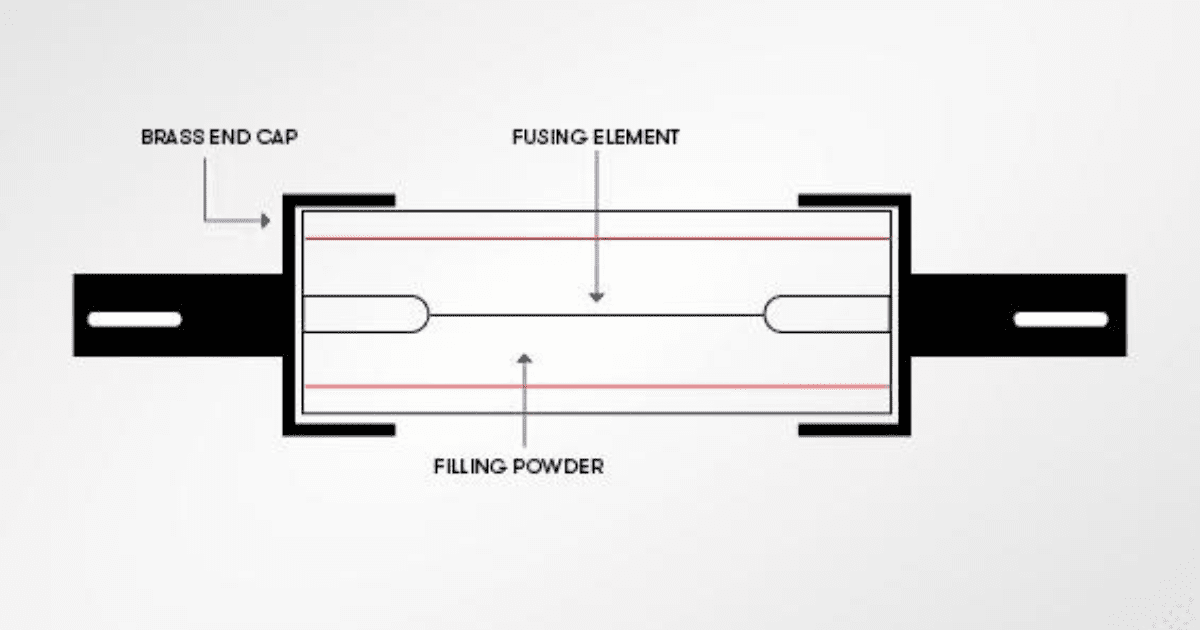
Fuse, as mentioned before, are made to rupture a fusible circuit in the event that an excessive amount of power passes through them. Every part of the circuit is shielded from harm in this way.
Based on your headlamp circuit setup, your low and high-beam headlamps could stop working if the HDLP fuse blows.
In the majority of cars, the high-beam and low-beam headlights on either the right or left side of the vehicle are fused separately, and the headlamp circuit comprises four relays. The high beam and low beam will both stop working if the HDLP fuse bursts in the event of an overcurrent or power surge.
Even if one of your vehicle’s two headlight fuses (HDLP #1 or #2) blows, the lights on the other fuse should continue to function normally, unless the second fuse is damaged.
Common issues with HDLP fuses
Because they do not blow more frequently than other automotive fuses, problems involving the HDLP fuse tend to go unnoticed and unreported. Having said that, I do have a few accounts from various individuals detailing their own encounters with an HDLP problem.
A 30-amp fuse with the designation HDLP wash was found by someone who was inspecting his trunk. Upon reviewing the owner’s manual, it was mentioned that the fuse was meant for a headlamp washer.
Unfortunately, a switch is not present. There is no toggle for this feature, you see. Using the windshield washer usually cycles the headlight washer on a number of vehicles that have one.
On the other hand, there’s a problem where the rocker switch lights up whenever the driver turns on the headlights for a 2012 Pete 384. You have up to 30 minutes of battery life before the headlamp turns on. In addition to the lights flickering while driving, the user reports that the car would display an HDLP problem on the dashboard.
After verifying the bulbs and pigtails, everything seemed to be in order, but another user reported seeing an HDLP fault notice on the dashboard. However, the clearance lights and headlights are still not working.
But, turning on the high-beam headlights is the sole way to trigger the HDLP issue. All of the connections appear to be in good working order after careful inspection. From time to time, the driver’s side low beam begins blinking. The high beam goes off entirely and the blinking begins after some time has passed.
Conclusion
The meaning of an HDLP fuse on a Chevy Silverado, a Ford, or any other make of vehicle is the same, as you may have guessed from reading this far. On every vehicle, you’ll find a headlamp fuse labeled HDLP. In addition to explaining how to test and replace the fuse, this page has detailed typical issues with this component.