Have you ever found yourself stranded because your car suddenly stopped working? It can be a frustrating and stressful experience. Knowing more about your car’s engine, the most important part of your vehicle, can help you avoid such situations. This article will guide you through the inner workings of the engine, its components, and how it works.
Understanding the Basics
Before diving into the details, let’s review some basic concepts about car engines. There are two main types of engines: gasoline and diesel. They both work on the same principle but have some differences.
Combustion Engine Types
A gasoline engine uses gasoline as fuel, while a diesel engine uses diesel. Both engines are called combustion engines because they burn fuel and air to create power. The difference between them is how they ignite the fuel and air mixture. A gasoline engine uses a spark plug, while a diesel engine relies on high pressure and temperature to ignite the fuel and air.
The Four-Stroke Cycle
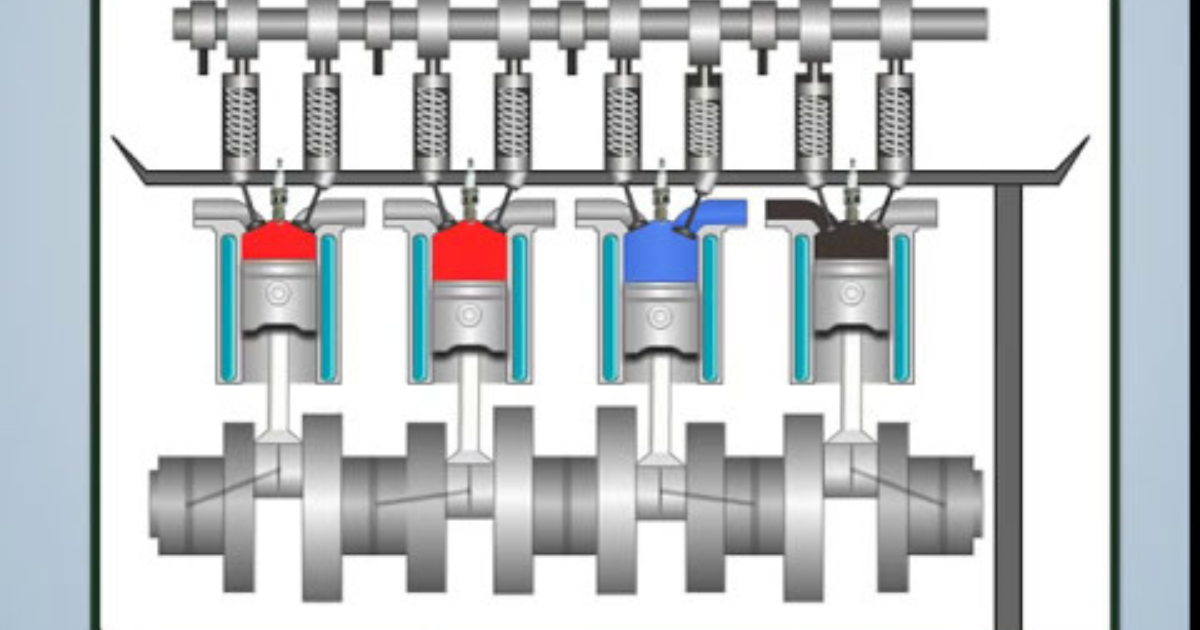
Both gasoline and diesel engines work in a similar way. They use a series of steps called the four-stroke cycle to create power. The four strokes are intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust.
Intake: The piston moves down and creates a vacuum inside the cylinder. This vacuum sucks a mixture of fuel and air into the cylinder through a valve.
Compression: The piston moves up and compresses the fuel and air mixture inside the cylinder. This increases the pressure and temperature of the mixture.
Combustion: The spark plug (for gasoline engines) or the fuel injector (for diesel engines) ignites the fuel and air mixture. The mixture explodes and creates a force that pushes the piston down.
Exhaust: The piston moves up again and pushes the waste gases out of the cylinder through another valve.
Key Components
Here are some of the key components of the engine that make the four-stroke cycle possible:
Pistons: These are metal cylinders that move up and down inside the cylinders.
Cylinders: These are metal tubes that hold the pistons.
Valves: These are metal flaps that open and close to let the fuel and air mixture in and the waste gases out of the cylinders.
Spark Plugs: These are small devices that create sparks to ignite the fuel and air mixture in gasoline engines.
Fuel Injectors: These are small devices that spray fuel into the cylinders of diesel engines.
Crankshaft: This is a metal shaft that connects the pistons and transfers their power to the wheels.
Power in Action
Now that you know the basics of how the engine works, let’s see how the engine transforms fuel and air into power and speed. We will look at four main systems that are involved in this process: the fuel system, the air intake system, the ignition system, and the exhaust system.
Fuel System
The fuel system is responsible for delivering fuel to the engine. It consists of the following parts:
Fuel Tank: This is where the fuel is stored.
Fuel Pump: This is a device that pumps fuel from the tank to the engine.
Fuel Filter: This is a device that filters out any dirt or debris from the fuel.
Fuel Lines: These are metal or plastic tubes that carry fuel from the tank to the engine.
Fuel Injectors or Carburetors: These are devices that mix fuel with air and deliver it to the cylinders.
Air Intake System
The air intake system is responsible for delivering air to the engine. It consists of the following parts:
Air Filter: This is a device that filters out any dust or dirt from the air.
Intake Manifold: This is a metal or plastic tube that carries air from the air filter to the cylinders.
Turbocharger or Supercharger: These are optional devices that increase the amount of air that enters the engine.
Ignition System
The ignition system is responsible for igniting the fuel and air mixture in the cylinders. It consists of the following parts:
Distributor: This is a device that distributes electrical signals to the spark plugs at the right time and order.
Spark Plugs: These are devices that create sparks to ignite the fuel and air mixture in the cylinders.
Ignition Coil: This is a device that transforms the low voltage from the battery into high voltage for the spark plugs.
Battery: This is a device that stores electrical energy and provides power to the ignition system and other parts of the car.
Exhaust System
The exhaust system is responsible for expelling the waste gases from the cylinders. It consists of the following parts:
Exhaust Manifold: This is a metal tube that collects the waste gases from the cylinders and sends them to the exhaust pipe.
Exhaust Pipe: This is a metal tube that carries the waste gases from the exhaust manifold to the tailpipe.
Tailpipe: This is the end of the exhaust pipe that releases the waste gases into the air.
Optimizing Engine Performance
Here are some simple tips for maintaining your engine and optimizing its performance:
- Change the oil and the oil filter regularly.
- Replace the air filter regularly.
- Check the spark plugs and the wires regularly.
- Inspect the belts and the hoses regularly.
By following these tips, you can ensure that your engine runs smoothly and efficiently.
Conclusion
In this article, we have learned how car engines work, the components that make up the engine, and how the engine transforms fuel and air into power and speed. By understanding how the engine works, you can appreciate your car more and enjoy driving it. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to contact us. We would love to hear from you and help you with your car’s engine. Thank you for reading and happy driving!