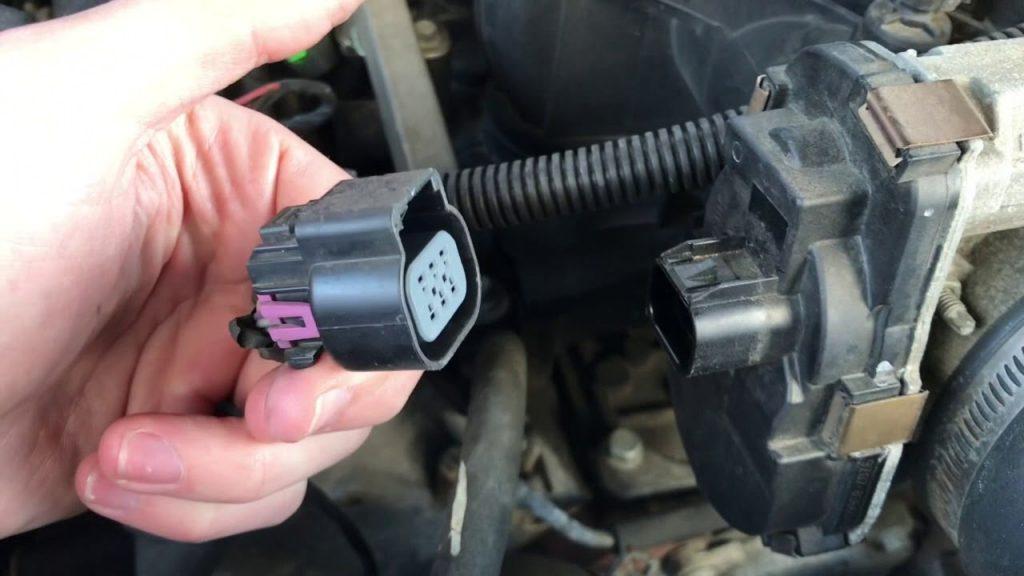
A bad throttle position sensor can cause a range of issues with your car, including shaking, poor acceleration, and trouble starting. This article will guide you through checking and replacing your throttle position sensor.
Understanding the Throttle Position Sensor
The TPS is typically located on the throttle body of the engine and is connected to the throttle plate shaft. It is a potentiometer that sends a voltage signal to the ECU based on the position of the throttle. This signal helps the ECU determine how much air is entering the engine so it can adjust the fuel injection accordingly.
Identifying a Faulty Throttle Position Sensor
If your vehicle is experiencing hesitation or other performance issues, the TPS may be to blame. Here are some signs that your TPS may be faulty:
- Hesitation or Stalling: You may notice a delay in acceleration or the engine stalling when you press the accelerator.
- Rough Idling: The engine may idle erratically or stall when at a stop.
- Poor Fuel Economy: A malfunctioning TPS can lead to inefficient fuel injection, resulting in poor fuel economy.
- Check Engine Light: The check engine light may illuminate, indicating a problem with the TPS or another component of the fuel injection system.
Testing and Replacing the Throttle Position Sensor
Here are three steps for replacing the throttle position sensor.
1. Locating the Throttle Position Sensor
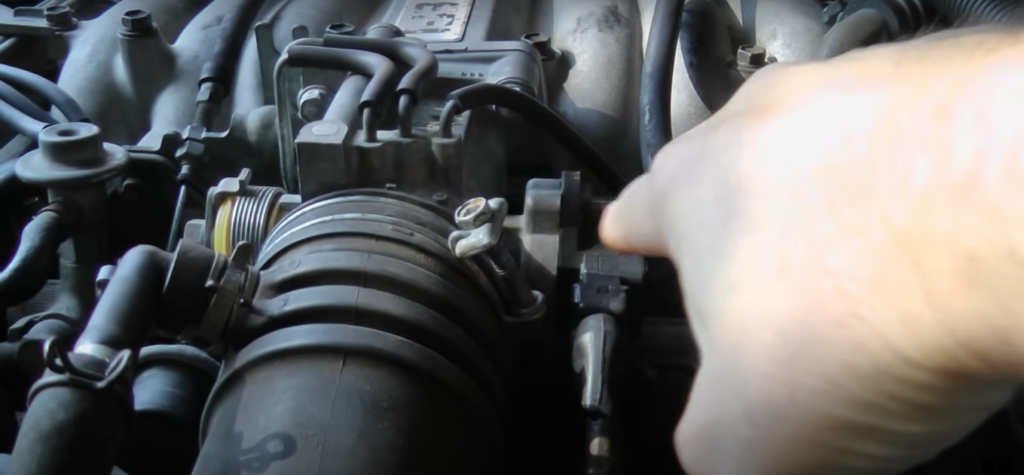

The location of the throttle position sensor varies depending on the make and model of your car. To locate the sensor in your car, consult your vehicle’s repair manual or search online for a guide specific to your car’s make and model.
2. Checking the Throttle Position Sensor
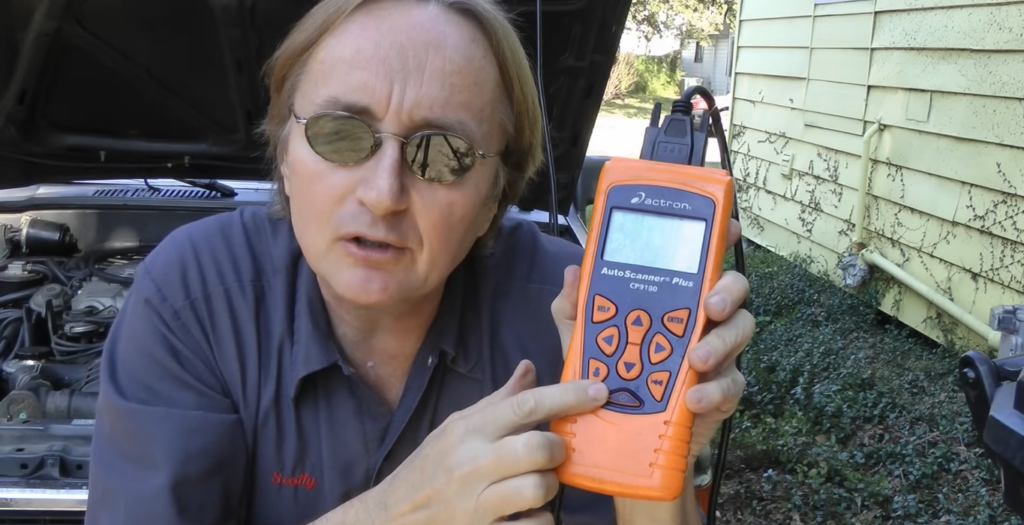

Modern cars (1996 or newer) can use an OBD2 analysis tool to examine throttle position sensor data. In older cars like the 1988 Toyota, a metal jumper wire is used to read engine codes with the check engine light. The code 41, indicates a problem with the throttle position sensor system.
To test the throttle position sensor, disconnect it with the engine running. If the engine runs better, the sensor is likely bad. However, it’s important to note that disconnecting the sensor while the engine is running can cause damage to some engines, so it’s recommended to consult your vehicle’s repair manual before attempting this test.
3. Replacing the Throttle Position Sensor
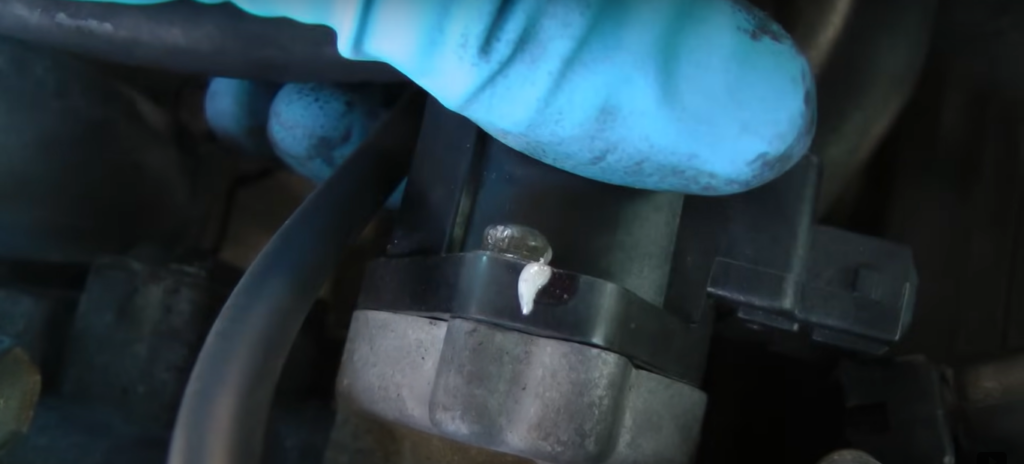

The sensor is removed by unscrewing two screws. However, use a small vice grip to loosen the screws as they may be stuck due to age. After removing the old sensor, aligns the new sensor and screws it into place.
A white mark is painted on the sensor to indicate the original position and aligns this mark with the screw head. The sensor is then fully tightened and the connector is plugged in.
Conclusion
A faulty throttle position sensor can cause various performance issues in your vehicle, including hesitation, stalling, and rough idling. By understanding the role of the TPS and knowing how to test and replace it, you can address these issues and ensure your car runs smoothly. If you’re unsure about diagnosing or replacing the TPS yourself, it’s best to consult a professional mechanic.