Is your car emitting a mysterious smoke? It could be a sign from your catalytic converter! Often overlooked, this vital component plays a crucial role in reducing harmful emissions, but when it starts smoking, it’s a red flag. From identifying the causes to exploring effective fixes, let’s dive into the world of catalytic converters. Learn how to spot the smoke signals and take action to ensure your vehicle’s health and environmental friendliness.
Catalytic converter smoking can be caused by several things, including oil leaks, bad spark plugs, clogged converter, mechanical failure, cracked cylinder head, or broken head gasket that will leave you with bad fuel economy and smoke from the tailpipe. It can be corrected and prevented by fixing the respective cause and regular maintenance.
What Is a Catalytic Converter?
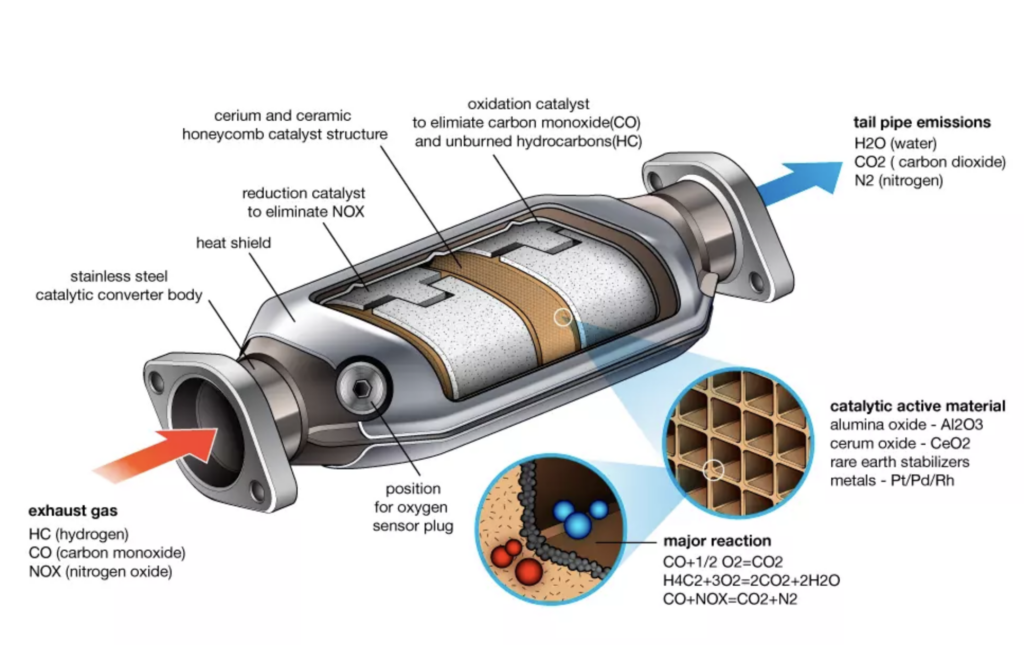
A catalytic converter is a device located in a car’s exhaust system. Its purpose is to reduce the harmful emissions produced by the car’s engine. It does this by converting harmful pollutants into less harmful substances before they are released into the environment.
The catalytic converter comprises a ceramic or metallic substrate coated with a mixture of precious metals such as platinum, palladium, and rhodium. These metals act as catalysts that help to break down pollutants in the exhaust.
Without a catalytic converter, car emissions would be much more environmentally harmful. It’s important to keep your catalytic converter in good working condition to ensure it’s doing its job.
What is Catalytic Converter Smoking?
Have you ever noticed smoke billowing out of a car’s tailpipe? This phenomenon is known as catalytic converter smoking. This is usually a sign of a problem with the catalytic converter, which can cause damage to the engine and the environment if left unaddressed. As a result, your engine’s performance will also be significantly hampered.
Understanding Smoke From Exhaust
When you notice smoke coming from your exhaust, it can be a cause for concern. However, the color of the smoke can give you an idea of what the issue may be. One specific color to look out for is white smoke.
This is typically an indicator of a coolant leak within your engine. It’s worth noting that white smoke can also be caused by a newly installed exhaust component or catalytic converter that is still adjusting.
It’s common to see some extra vapor during cold weather, but it should disappear shortly after. Keep an eye out for excessive white smoke, which could signify a more serious issue.
Does a Catalytic Converter Generate White Smoke?
A damaged catalytic converter can be the root of white smoke issues, but it’s not the catalytic converters that cause this problem. Generally, other factors related to the catalytic converters are responsible for this, such as:
- Condensation
- Clogged catalytic converter
- Malfunctioning fuel delivery systems
- A blown head gasket
- Cracked cylinder head
All these elements must be present for a catalytic converter to generate white smoke. It is rare for cats to emit this type of smoke without outside interference; however, they can emit hazardous chemicals and black exhaust if not properly maintained.
What Causes The Catalytic Converter Smoking?
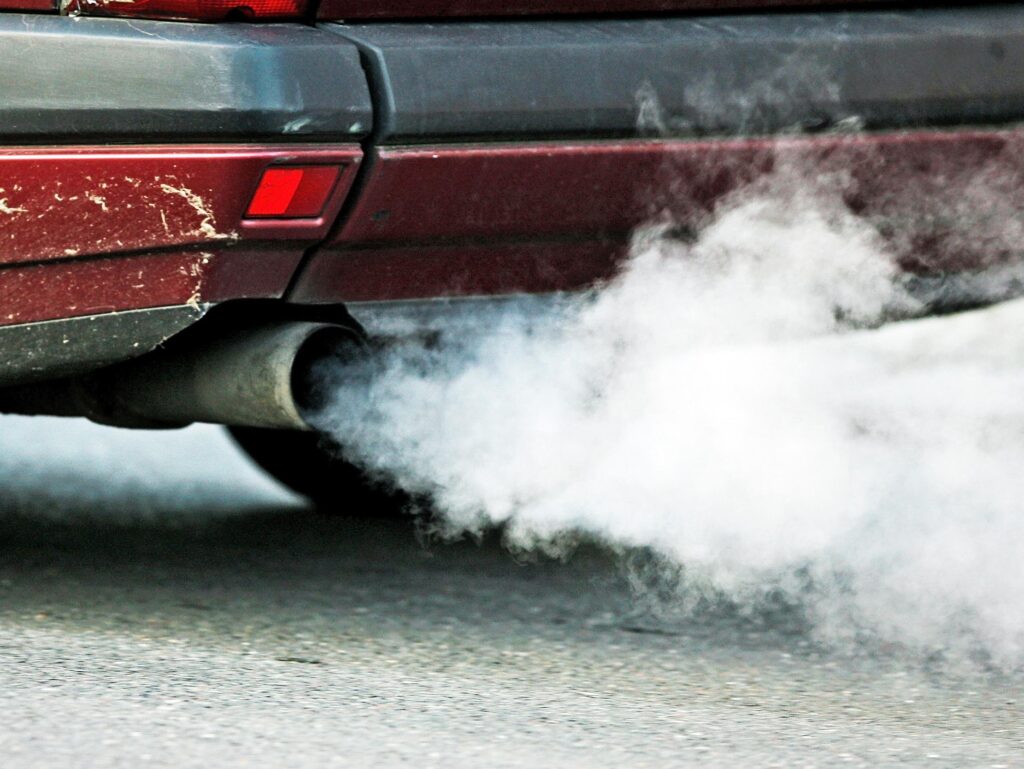

There are several reasons why a catalytic converter can smoke, including:
Clogged Catalytic Converter
The catalytic converter can become clogged with debris or carbon build-up. This can happen when the car is driven primarily on short trips, where the engine does not get hot enough to burn off the debris. A clogged converter can cause the exhaust to back up, causing smoke to come out of the tailpipe.
Blown Head Gasket
In the event that the gasket was to blow out, coolant would flow into the catalytic converter. As we know, coolant is an aqueous formation that, upon heating up and evaporating, produces smoke in its vapor state. The result: more smoke billowing out of your exhaust pipe!
Mechanical Failure
The failure of the catalytic converter mechanically can cause smoke to come out of the exhaust. This can happen if the converter is damaged or the exhaust pipe is not sealed correctly.
Overheating of the engine
The catalytic converter can become overheated if the engine is running too hot. A malfunctioning thermostat, a clogged air filter, or a leaking head gasket can cause this. When the converter overheats, the precious metals inside can melt, causing smoke to come out of the exhaust.
Oil Leaks
The oil that leaks from the engine can get into the catalytic converter, which can cause the converter to break down and smoke. Oil leakage also signals other faults, so it is important to give them full attention.
Cracked Cylinder Head
A broken cylinder head or block can cause coolant to enter the combustion chamber and eventually reach the catalytic converter, which will evaporate and result in a blowing smoke effect – just like a blown head gasket.
Faulty Oxygen Sensors
Oxygen sensors are responsible for measuring the amount of oxygen in the exhaust system, and if they are not working properly, they can cause the catalytic converter to smoke.
Use of incorrect fuel
Using the wrong fuel type, such as leaded gasoline, can cause damage to the catalytic converter. This can cause the converter to smoke or even fail completely.
Bad Spark Plugs and Ignition Systems
Spark plugs are responsible for providing the spark that starts the engine, and if they are not working properly, they can cause the catalytic converter to smoke due to incomplete combustion of the fuel.
What Are the Symptoms of Catalytic Converter Smoking?
Catalytic Converter Smoking - Causes, Signs and FixWhen a catalytic converter is smoking, several symptoms can occur. These include:
Increased Fuel Consumption
A smoking catalytic converter can cause the engine to work harder, which increases fuel consumption. Among other factors to pinpoint for increased fuel consumption, catalytic converter smoking is one of the most significant ones.
Bad Fuel Economy
A smoking catalytic converter can decrease fuel efficiency, causing the car to consume more gas and travel less distance on a full tank.
Smoke Coming From the Tailpipe
This is the most obvious symptom of a smoking catalytic converter. Smoke comes out of the tailpipe of the car. The smoke can be white, blue, or black, depending on the cause of the problem.
Reduced Engine Performance
A smoking catalytic converter can negatively impact the performance of the engine. This can manifest in a power reduction, making it harder to drive the car.
Warning Lights on the Dashboard
If the catalytic converter is smoking, warning lights on the car’s dashboard can be observed, indicating a problem with the converter.
Bad Odor
When a catalytic converter is smoking, it can release an unpleasant smell that can be unpleasant for the driver and passengers alike.
How to Test Catalytic Converter?

There are several ways to test a catalytic converter to determine if it works properly. Here are a few methods:
Back Pressure Test
This test measures the amount of pressure that is building up in the exhaust system. If the pressure is too high, it could indicate that the catalytic converter is clogged or malfunctioning.
Oxygen Sensor Test
This test checks the oxygen sensors in the exhaust system to determine if they are working properly. If the sensors are not working correctly, it could indicate that the catalytic converter is not doing its job.
Visual Inspection
A visual inspection of the catalytic converter can reveal any physical damage or corrosion causing problems.
Scan Tool
A scan tool can check the engine’s computer system for any diagnostic trouble codes indicating a problem with the catalytic converter.
Poor Idling
If the catalytic converter is smoking, the car may idle poorly, which can be observed as the car shaking or vibrating while idling.
Tailpipe Test
A tailpipe test can measure the emissions coming out of the tailpipe. High carbon monoxide and hydrocarbon levels can indicate a problem with the catalytic converter.
It is always recommended to consult a professional mechanic to diagnose and test the catalytic converter, as they have the right tools and equipment.
How to Fix Catalytic Converter Smoking?

If you notice any of the symptoms of catalytic converter smoking, it’s important to get the problem fixed as soon as possible. There are several solutions for catalytic converter smoking, including:
Replace the Catalytic Converter
The catalytic converter must be replaced if it is damaged or beyond repair. This can be costly, but it is the most effective solution to fix the problem.
Fixing Engine Overheating
An overheating engine can severely damage the catalytic converter if left unaddressed. To prevent this, it’s crucial to take immediate action. This can include checking the coolant levels and replacing the coolant if needed, inspecting the radiator and hoses for leaks, and ensuring the thermostat is functioning properly.
Replacing Faulty Oxygen Sensors
If the oxygen sensors are faulty, it is important to replace them as soon as possible to prevent further damage to the catalytic converter. This can be done by having a mechanic check the sensors and replace them if necessary.
Fixing Oil Leaks
An oil leak can cause serious damage to the catalytic converter if left unresolved. To prevent this, it’s essential to take immediate action. This can include checking the oil levels and replacing the oil if needed, inspecting the oil filter and oil pan for leaks, and making sure the oil pump is functioning properly.
Clearing Clogged Catalytic Converter
When a catalytic converter becomes clogged, prompt action is crucial to avoid further damage to the converter. The best way to address this issue is by having a professional mechanic inspect the converter and perform the necessary cleaning procedures.
Using the Correct Fuel
Using the correct fuel type for your vehicle is important to prevent damage to the catalytic converter. This means using unleaded gasoline in vehicles that are designed to use it.
Replacing Bad Spark Plugs and Ignition Systems
If the spark plugs or ignition system is not working properly, it is important to replace them as soon as possible to prevent further damage to the catalytic converter. This can be done by having a mechanic check the spark plugs and ignition system and replace them if necessary.
Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance can prevent catalytic converter smoking by keeping the engine and exhaust system in good working condition. This includes regular oil changes, air filter replacements, and regular inspections of the exhaust system.
Is It Possible for a Catalytic Converter to Clean Itself?
No, a catalytic converter cannot unclog itself. Over time, the catalytic converter can become clogged with debris and exhaust buildup, reducing its efficiency. This clogging can be caused by a variety of factors, including an incorrect fuel/air mixture, engine misfires, and oil contamination. In order to resolve the issue, the clogged catalytic converter needs to be physically removed and cleaned or replaced.
How Long Do Catalytic Converters Last?
Catalytic converters typically last between 70,000 and 100,000 miles. However, the lifespan of a catalytic converter can vary depending on several factors, including
- The type of car
- The driving conditions
- The quality of the converter
A catalytic converter installed in a car driven mainly on the highway is likely to last longer than a converter driven primarily in the city. This is because highway driving produces less wear and tear on the converter than city driving.
Another factor that can affect the lifespan of a catalytic converter is the quality of the converter. High-quality converters are typically made of better materials and are built to last longer than low-quality converters.
It’s also worth noting that if a vehicle has been running on poor-quality fuel or has had a history of misfires, it can damage the catalytic converter and reduce its lifespan.
It’s important to keep your vehicle well-maintained and have regular check-ups to ensure that the catalytic converter is working properly and to avoid any issues that could shorten its lifespan.
Conclusion
Catalytic converter smoking is a serious problem that can cause damage to the engine and the environment. However, by understanding the causes and solutions for catalytic converter smoking, you can take steps to prevent or fix the problem. If you notice any symptoms of catalytic converter smoking, it’s important to have your vehicle inspected by a professional mechanic as soon as possible. Regular maintenance and using the correct fuel can also help prevent catalytic converter smoking and ensure your vehicle runs at its best!