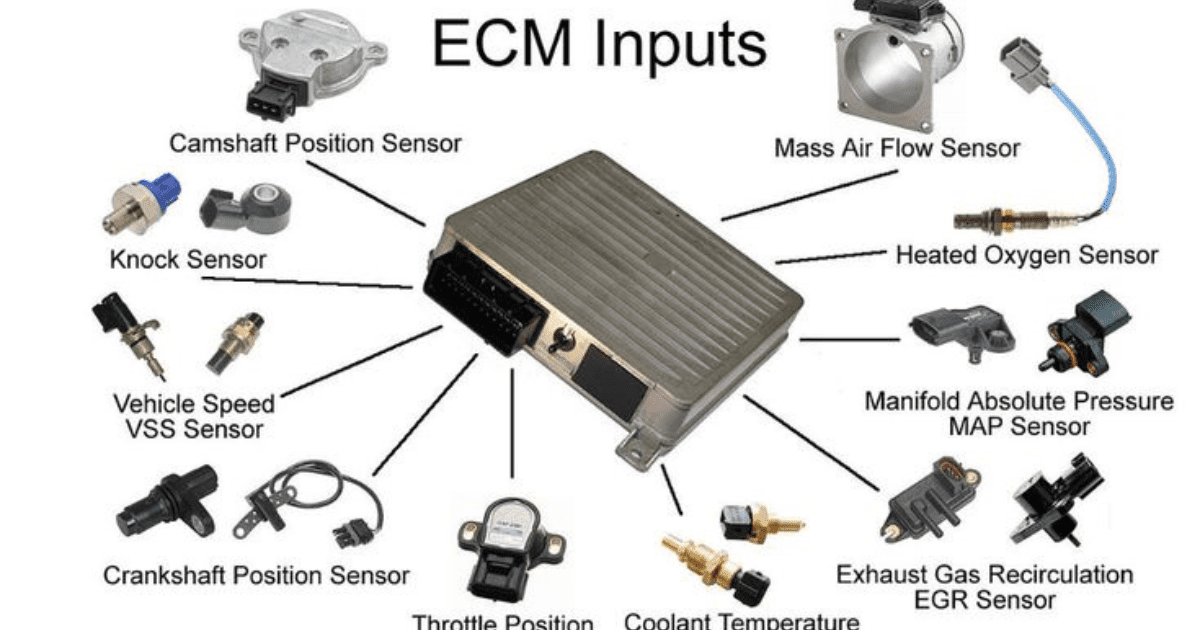
The Engine Control Unit (ECU) is a very important part of car technology that you need to understand. This study looks into the complicated web of how inputs, outputs, and sensors work together to figure out how to make an engine run at its best.
An Engine Control Unit (ECU) is a computerized control module that in modern cars handles how the engine and its parts work. Its inputs and outputs, as well as how the different sensors work together, are shown below in point form:
Inputs to the ECU:
- The throttle position sensor (TPS) checks the gas pedal’s position to figure out how much air and fuel the engine needs.
- The mass airflow monitor (MAF) checks how much air is entering the engine so that the fuel injection can be set correctly.
- An oxygen monitor (O2) checks how much oxygen is in the exhaust to help keep the air-to-fuel ratio in check.
- The coolant temperature sensor (CTS) checks the coolant temperature to change the speed of the spark plugs and fuel injection.
- The crankshaft position monitor (CKP) finds the crankshaft’s position and speed so that the timing of the fuel injection and ignition can be set.
Outputs from the ECU:
- Fuel injectors are used to feed fuel to the engine.
- Ignition coils to make the spark that the fuel mixture needs to catch fire.
- An idle air control (IAC) valve lets you change how much air goes into the engine when it’s not running.
- A variable valve timing (VVT) system lets you change when the intake and exhaust valves open and close to get the best performance.
- A transmission control module (TCM) that sets how the automatic gear shifts.
How different sensors work together:
- Both the TPS and MAF sensors tell the engine how much air and fuel it needs at any given time.
- The O2 monitor tells the ECU how much oxygen is in the exhaust, which helps keep the air-to-fuel ratio in check.
- The CTS helps the ECU change the speed of the spark plugs and fuel injection based on the temperature of the engine.
- The CKP sensor tells the ECU where the crankshaft is and how fast it is turning. This helps the ECU set the best time for the ignition and fuel injection.
- These sensors help the ECU control the engine’s performance, making sure that the fuel economy, power output, and emissions are all at their best.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the ECU is an important part of a modern car that controls the engine’s performance with many monitors and output devices. Some of the things that go into the ECU are sensors that record the crankshaft position, airflow, oxygen level, throttle position, and engine temperature. The ECU sends signals to the ignition coils, fuel injectors, idle air control valve, variable valve timing system, and transmission control module. These parts are controlled by the signals. These outputs and sensors work together to keep the engine running smoothly and efficiently.