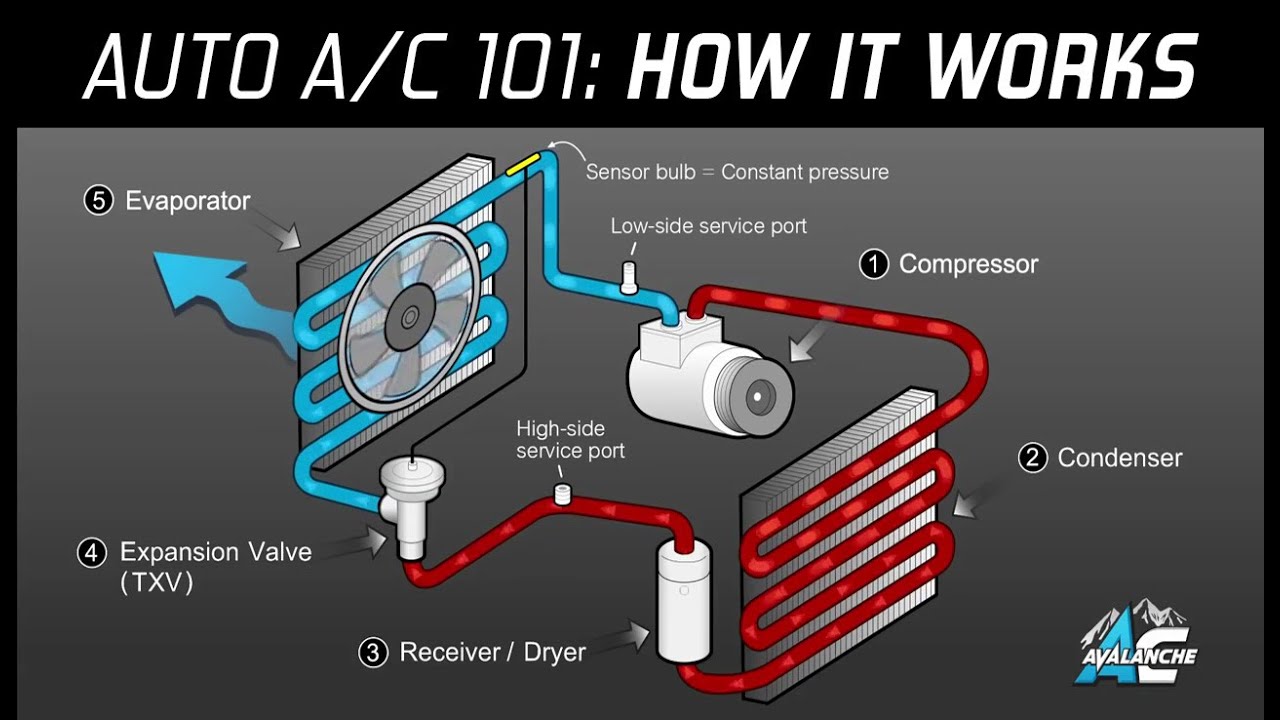
Ever wonder how your car’s air conditioning system works? Well, it all comes down to refrigeration! Every component in a car’s refrigeration cycle, from the compressor to the condenser, plays an important role. In this article, we will explore these components and how they work together to provide cool, refreshing air on hot summer days.
How Does the Car AC System Work?
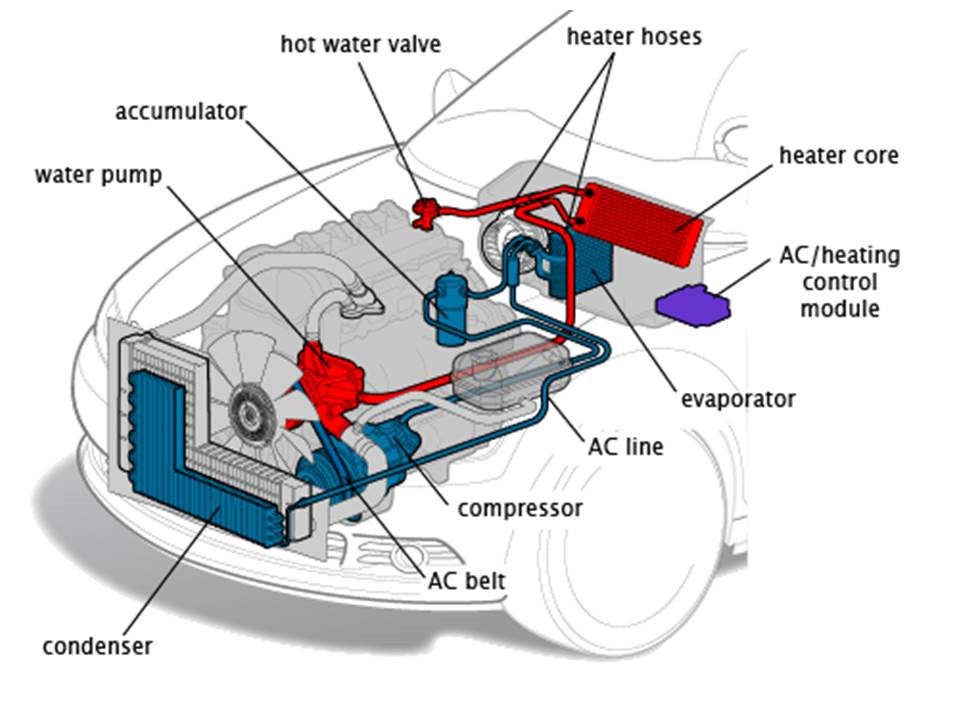
AC in cars stands for air conditioning and is a system used to control the temperature inside the car. A compressor powers it and allows the driver to adjust the air from cold to warm to cool down or heat the vehicle’s interior.
The main concept of the AC system is based on the principle of refrigeration, which involves removing heat from the air and transferring it outside the vehicle. The AC system includes components such as the compressor, condenser, evaporator, and expansion valve.
Components of the AC car system
- Compressor: The compressor pumps out cooled refrigerant, passing through the condenser, evaporator, and expansion valve.
- Condenser: It cools and condenses the warm air from the interior.
- Evaporator: It evaporates the hot air and returns it to the interior.
- Expansion valve: The expansion valve increases the pressure of the refrigerant, allowing it to move better through the system.
- Receiver-Dryer: Used between evaporator and compressor to convert any remaining liquid into vapors before sending it to the compressor for compression.
- Refrigerant: The heat-sensitive fluid with a shallow boiling point used in AC as a heat exchange medium.
- Pressure Regulating Devices: Controls the temperature in the evaporator.
- Orifice Tube: Located in the inlet tube of the evaporator, it changes air from hot to cold.
- Accumulator: Connected directly to the evaporator outlet and stores excess liquid refrigerant.